Hexadecimal and decimal systems
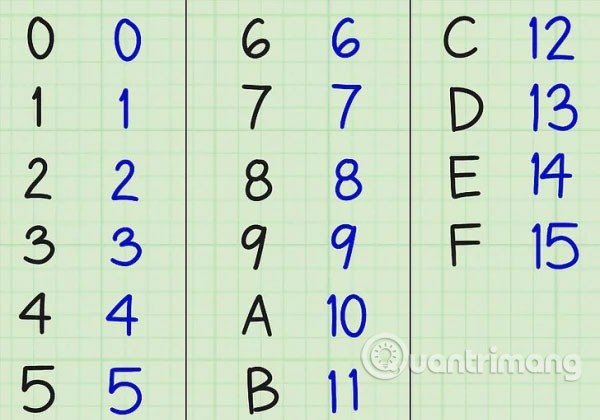
The hexadecimal system has 16 digits. The digits 1 through 9 are the same as in the decimal system, then the decimal numbers 10 through 15 are replaced by the letters A, B, C, D, E, and F of the English alphabet.
The decimal system (also known as the base 10 system) is a standard system for representing integers and non-integer numbers (decimal numbers). It is an extension for non-integer numbers of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system.
How to convert base 16 to base 10
Hex is a base 16 number system and decimal is a base 10 number system. Sometimes, we need to know the decimal equivalent of a hexadecimal number.
Here are the steps to convert from base 16 to base 10:
- Get the decimal equivalent of the hexadecimal digit from the table.
- Multiply each digit by the power of 16 (the exponent corresponds to the digit's position, the rightmost digit corresponds to the 0 position). For example, in 7DE, the E position is 0, the D position is 1, and the 7 position is 2.
- Calculate the sum of all multiplications.
Here is an example:
7DE is a hexadecimal number
- 7DE = (7 * 162) + (13 * 161) + (14 * 160)
- 7DE = (7 * 256) + (13 * 16) + (14 * 1)
- 7DE = 1792 + 208 + 14
7DE = 2014 (in decimal)
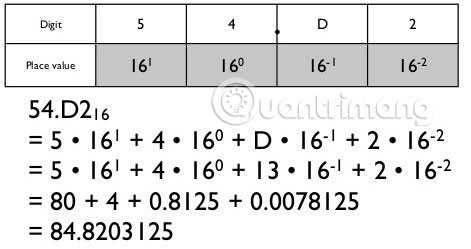
Example of converting from base 16 to base 10:
- (1D9)16 = (473)10
- (80E1)16 = (32993)10
- (10CE)16 = (4302)10
Conversion table from base 16 to base 10
| Hexadecimal system |
Base 10 system |
| 0 |
0 |
| 1 |
1 |
| 2 |
2 |
| 3 |
3 |
| 4 |
4 |
| 5 |
5 |
| 6 |
6 |
| 7 |
7 |
| 8 |
8 |
| 9 |
9 |
| A |
10 |
| B |
11 |
| C |
12 |
| D |
13 |
| E |
14 |
| F |
15 |
See also: