How to use the ipconfig command to refresh, reset IP address
This article will guide you how to use ipconfig to find IP address, reset IP address as well as assign new IP address.
If you want to send a letter, you need the recipient's address. The address is the identifier that tells the postman where to send the letter, so the address must be unique. Two houses cannot have the same address, otherwise there will be confusion.
The Internet works much like the postal service. Instead of sending letters, devices send “packets of data,” and IP addresses or MAC addresses determine where those packets will go. Today’s article will discuss how the two work together.
Table of Contents of the Article
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a numerical identifier for a piece of network hardware. Devices on a network have unique IP addresses, similar to home or business addresses. Devices use IP addresses to communicate with each other over a network.
Quantrimang has a long article about IP addresses, for more details, please read the article: What is an IP address?
A MAC address uniquely identifies a "network interface" in a device. While IP addresses are assigned by the ISP and can be reassigned when a device connects or disconnects, MAC addresses are tied to the physical adapter and are assigned by the manufacturer.
A MAC address is a string of 12 digits, where each digit can be any number from 0 to 9 or a letter from A to F. For readability, the string is divided into blocks. There are three common formats, the first of which is the most common and preferred:
The first 6 digits (called the “prefix”) represent the adapter manufacturer, while the last 6 digits represent a unique identifier for that particular adapter. The MAC address does not contain information about which network the device is connected to.
Although MAC addresses and IP addresses have many differences, they do not operate independently of each other. The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is the bridge that connects them. This protocol operates between Layer 2 and Layer 3 on a local area network (LAN) . It maps IPv4 addresses to the MAC addresses of network devices and vice versa.
Note : IPv4 uses the ARP protocol. On newer IPv6 networks, the Neighbor Discovery Protocol provides equivalent functionality.
Here's how it works: A device wants to communicate with another device on a local network segment. It puts its request with both the source IP address and the destination IP address in an IP packet. An Ethernet frame then encapsulates the IP packet. This frame contains both the source and destination MAC addresses. But sometimes the destination device's MAC address is unknown.
Computer A wants to send an IP packet to computer B. But it does not know the MAC address of computer B. Computer A then broadcasts an ARP request which is received by all computers in the local network segment.
Basically, the request says, “Here is my IP address. Here is my MAC address. And I'm looking for the MAC address associated with this IP address. If this IP address is yours, please respond and give me your MAC address.”
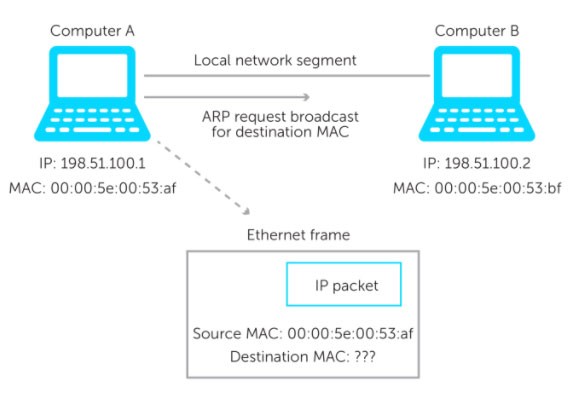
Computer B receives the ARP request and will do two things.
First, every device has its own ARP table. Whenever a computer wants to send a packet on a LAN, it will first look in its ARP table. If an entry for Computer A does not already exist in the Computer B table, it will create a new entry. Computer A's MAC and IP addresses will be added based on what is in the frame.
An ARP response with the IP address and MAC address will then be sent. Computer A will receive the response and add the information to its ARP table. With the matching MAC address, Computer A can now send an Ethernet frame to Computer B.
It is important to note that, although the IP address is easy for anyone to look up, the MAC address is not easy for others to find. When an IP packet leaves your LAN and passes through a router, its header with the MAC address is stripped away. Therefore, anyone outside the LAN will never see your MAC in the IP packet (unless an application sends it as data).
Because they are assigned to the NIC or other hardware, MAC addresses never change themselves (but many network interfaces support MAC address changing). On the other hand, many IP addresses are dynamic, changing periodically based on time or characteristics of the network setup.
A MAC address is a 48-bit hexadecimal address. It is typically made up of six sets of two digits or characters, separated by colons. An example MAC address would look like this: 00:00:5e:00:53:af.
Many network card and other hardware manufacturers use a similar string at the beginning of the MAC address of their products. This is called an organizationally unique identifier (OUI). The OUI is usually the first 3 bytes of a number or character. The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) manages the OUIs for manufacturers.
Meanwhile, an IPv4 address is a 32-bit integer represented in hexadecimal notation. A more common format, known as dotted quad or dotted decimal, is xxxx, where each x can be any value between 0 and 255. For example, 192.0.2.146 is a valid IPv4 address.
MAC addresses and IP addresses also exist in different layers of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. The OSI model is a conceptual framework that uses seven abstract layers to describe all the functions of a telecommunications system. In the OSI model, the MAC sublayer of the data link layer (Layer 2) implements MAC addresses. Whereas, an IP address operates in the network layer (Layer 3) of the model.
Remember how an IP address represents a device's connection to an ISP? What if a second device connects to the primary device and channels all web activity through that device? To the rest of the web, the second device's activity appears to be the primary device.
This is how you hide your IP address from others. While there is nothing wrong with doing this, it can lead to security issues. For example, a malicious hacker hiding behind some proxy can make it very difficult for the authorities to track him down.
Another risk is that IP addresses can be traced . You'd be surprised what someone can do with just your IP address.
And there's also the potential problem of IP conflicts , where two or more devices share the same IP address. This mostly happens within a local network, but with the growing shortage of IPv4 addresses, it could soon spread across the entire Internet.
As for MAC addresses, there’s really only one problem you need to be aware of: It’s incredibly easy to change a device’s MAC address . This defeats the purpose of a unique manufacturer-assigned identifier, since anyone can “spoof” someone else’s MAC address. It also makes features like MAC filtering virtually useless.
Regardless, IP addresses and MAC addresses are useful and important, so they aren’t going away anytime soon. Hopefully now you understand what they are, how they work, and why you need them.
If you have any questions or if you have any other tips or explanations, please share them with us in the comments section below!
See also:
This article will guide you how to use ipconfig to find IP address, reset IP address as well as assign new IP address.
To ensure better security, devices running Android 10 and above will use random WiFi MAC addresses by default.
Tired of Microsoft Teams workflows and Power Automate errors halting your productivity? Get step-by-step solutions to common issues like authentication failures, timeouts, and flow errors. Fix them in minutes and automate effortlessly!
Facing Microsoft Teams "Download Error" on MacBook? Discover proven troubleshooting steps to resolve download failures quickly, from cache clears to reinstalls, and get back to smooth teamwork.
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Where is Teams" Folder Error? Discover proven, step-by-step troubleshooting fixes to resolve it quickly and restore smooth teamwork. Latest methods included!
Frustrated by Microsoft Teams JavaScript Error on desktop app? Discover proven steps to fix it fast: clear cache, update, reset, and reinstall. Get back to seamless collaboration in minutes!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Guest Login" Error? Discover step-by-step fixes, from quick cache clears to admin settings, to resolve guest access issues fast and collaborate seamlessly. Updated with the latest tips!
Tired of the Microsoft Teams "For PC" download error blocking your work? Follow our proven, step-by-step guide to resolve it quickly and get Teams running smoothly on your PC today.
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Windows 7" login error? Discover step-by-step fixes for this frustrating issue on Windows 10/11. Clear cache, edit registry, and more – get back to seamless collaboration today!
Tired of Microsoft Teams Error Code 0x80070005 blocking your meetings? Follow this 2026 guide with step-by-step fixes for access denied issues. Get Teams running smoothly in minutes!
Master the installation of the Microsoft Teams Add-in for Outlook 2026 effortlessly. Boost your productivity with seamless scheduling and meetings. Follow our proven, up-to-date steps for instant success!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "License Error" 2026? Discover proven, step-by-step solutions to resolve it fast. Clear cache, check licenses, and get back to seamless collaboration—no IT help needed!
Whether youre in your 50s, 60s, or even 70s, its not too late to prioritize your health and put yourself first. Here are the best exercises for people 50 and older.
Struggling with Microsoft Teams Error Caa50024 on Windows 10/11? Follow our step-by-step fixes to resolve crashes and launch issues quickly. Latest proven solutions for seamless teamwork.
Stuck with Microsoft Teams login error AADSTS50011? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes to resolve the reply URL mismatch issue and log in seamlessly. No tech skills needed!
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Win 7" Compatibility Error blocking your meetings? Get instant fixes with our step-by-step guide, including workarounds for older Windows versions. Resolve it now and stay connected!
Tired of the endless Microsoft Teams "Error R" restart loop? Get step-by-step fixes to solve Microsoft Teams Error R quickly. Clear cache, reset, reinstall & more for smooth collaboration. Works on Windows, Mac & web.