CPU stands for a word that refers to a processor capable of computing from which to process data, this is an indispensable component for a PC computer, but how are they actually made and how are they made? What components can produce CPU like today? Invite you and WebTech360 PC to learn it.
The CPU is abbreviated as Central Prossesing Unit, also known as the data processing center, or simply understood, it is the brain that controls most of the remaining components in a computer set. The function of the CPU is to process and analyze any data as it is entered into it, and it will handle any computation requests from the computer user. In addition, please refer to the genuine Intel and AMD CPU lines at WebTech360 .
1. What are the components of a CPU?
- The controller (Control Unit) is the microprocessor that is responsible for interpreting the instructions of the Control Program, which is regulated by the measured clocks of the system clock.
- The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU-Arithmetic Logic Unit) has the function of executing the instructions of the control and signal processing unit. By name. then this unit arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and comparison operations like greater than and less than...
- Register is responsible for recording the instruction set before and after processing.
As at the present time, the Microprocessors (CPUs) have a very high default clock that allows for faster and better calculations, in addition, today's CPUs are also equipped with Hyper Threading technology . ) uses processor resources more efficiently, allowing more threads per CPU core.
2. CPU specifications
The processing speed of the external CPU depends on the clock levels and cache inside it, the combined components such as Main , Ram, Hard drive will also decide and constitute a complete machine. The higher the CPU clock, the higher the Ram Bus and the higher the SSD read and write speed, the bigger the computer.
FSB - (Front Side Bus): Is the speed of data transmission in and out of the CPU or the speed at which data runs through the pins of the CPU. Cache memory: The memory area that the CPU uses to store parts of programs and documents. about to be used. When needed, the CPU will look for information on the cache before looking in the main memory.
3. How many cores does the CPU have?
When CPUs were introduced, they only had a single core, making computations often relatively slow and time-consuming, but enough to change the world at the time. After pushing the single-core CPU to its limits, manufacturers began to look for new ways to improve performance. This move to improve performance led to the creation of multi-core processors. These days, you'll often hear terms like dual-core, quad-core, and multi-core (or multi-core).
For example, a dual-core processor is really just two separate CPUs on a single chip. By increasing the number of cores, the CPU can handle multiple processes concurrently. This is effective against the desire to increase performance and reduce processing time.
Dual-core processors soon gave way to 4-core processors with 4 CPUs, and even multi-core processors with 8 CPUs. Add to the hyperthreading technology that your computers can perform tasks as if they had up to 16 cores.
4. How does the CPU work?
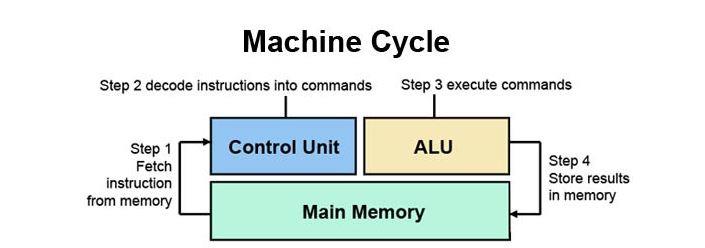
After many improvements, the CPU still keeps the basic functions and the CPU works through 3 steps: Fetch, decode and execute.
Fetch
Just as you would expect, the fetching process involves receiving a command. The instruction is represented as a string of numbers and is passed to the CPU from RAM. Each instruction is only a small part of any operation, so the CPU needs to know which instruction is coming next. The current instruction address is held by a Program Counter - the program counter (PC). The PC and instructions are then placed in an Instruction Register - the instruction register (IR). The length of PC is then incremented to refer to the address of the next instruction.
Decryption
When an instruction is fetched and stored in the IR, the CPU transmits the instruction to a circuit called the instruction decoder. This converts the instruction into signals that are passed through to other parts of the CPU to perform the action.
Enforcement
In the final step, the instructions are decoded, sent to the relevant parts of the CPU to be executed. The results are usually written to a CPU register, where they can be referenced by subsequent instructions. Think of it like the function of memory on a computer.
5. Popular CPUs in the last few years
Currently, the two largest global CPU manufacturers are AMD and INTEL. Since mid-2017, AMD 's strong comeback has helped users always have very stable and secure choices. The competition from these two biggest brands gives users more choices.
Current popular socket codes. There are Socket 1150, 1151, 1151V2 and socket lines 2011 and 2066 equivalent to Haswell , skylake, kabylake and the latest and popular now is Coffelake which are the socket lines of intel CPUs.
And now AMD is popular with the AM4 and TR4 . socket series
Some popular Intel CPU lines such as Intel Core i3, i5, i7, i9 and Intel Xeon are favored and chosen by many customers. For AMD some popular CPU lines such as: AMD Ryzen 5, AMD Ryzen 7 and AMD Ryzen threadripper are also well received and used by many users.
Some of the most popular Intel CPUs today are:
Some AMD CPUs are popular with many customers:
6. How important is the CPU?
While the CPU is not as important to system performance as it used to be, it still plays a major role in making the device run fast. Since it is only responsible for executing instructions in programs, the faster your CPU, the faster many applications will run.
That said, a fast CPU isn't everything. The processor, no matter how powerful, cannot easily render the latest 3D games nor can it store information. That's where other components, like the graphics card and memory, come into play.
In short, CPU is not everything, but it is very important. Generally speaking, a faster CPU means your system or device will run faster. At least it won't be a bottleneck in its own right. Multiple cores and threads can help you do many things at once.