Android Debug Bridge aka ADB is a powerful and versatile tool that allows users to do many things like find logs, install and uninstall apps, transfer files, root and flash custom ROMs, create device backups, and more. In fact, most advanced tutorials and guides on how to do something on Android tend to use adb commands to get the job done.
Furthermore, adb is also very useful when your Android device is not working as it should or when things are just too messy and unusable. Although it looks a bit “scary” and complicated, here is a list of adb commands to get you started and do some useful things in processes.
21 Useful ADB Commands on Android
Unlike previous versions, users do not need to install the full Android SDK to install ADB. Just download the standalone ADB zip file, extract it to the root of the C drive and you are done. To access adb, open Command Prompt by searching for it in the Start menu and navigate to the adb folder using the command below. If you have installed adb in a different folder, change the command accordingly.
cd c:\adb
Tip: Then, open a Command Prompt from the same folder, press and hold the Shift key, then right-click on the folder, and then click on the “ Open command prompt here ” option .
Now, connect your Android device via USB and proceed to test the commands below.
Commonly used ADB commands
1. Start or stop ADB server
Obviously, the first command to know is how to start and stop the adb server. This allows the user to interact with the connected Android device. To start the adb server, use the command below.
adb start-server
Once done with its work, the user can use the command below to stop the adb server.
adb kill-server
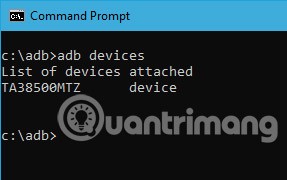
2. List connected Android devices
This is one of the most common commands. When connecting a device to your computer via USB, use this command to verify that adb can find the connected device.
adb devices
If the device is properly connected to the system, the above command will start the service daemon, scan the system and list all the connected Android drives. The best part about this command is that it lists both the status of the devices and their serial numbers.
3. Know the status of the device
As the name suggests, this command can be used to know the device status. When the command is executed, it will display whether the device status is offline, bootloader or device. For a normal Android device, the user will see their Android status as “device”, as shown in the image below.
adb get-state
4. Display device serial number
This command tells the user the serial number of the connected device. On a phone or tablet, the user can see the device serial number by navigating to “ Settings > About Phone > Status ”.
adb get-serialno
5. Copy files from computer to phone
If you want to copy files from your computer to your phone using adb, you can use this command. Don't forget to replace [source] and [destination] with the actual file path.
adb push [source] [destination]
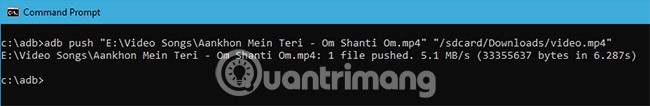
When you replace the above command with the actual file path, it will look like this.
adb push "E:\Video Songs\Aankhon Mein Teri - Om Shanti Om.mp4" "/sdcard/Downloads/video.mp4"
6. Copy files from phone to computer
Just like copying files from your computer to your Android device, you can also copy files from your phone to your computer. To do that, just use the command below. Replace [source] and [destination] with the actual file path.
adb pull [source] [destination]
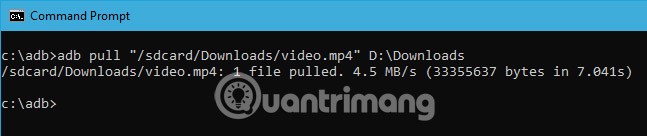
When replacing the above command with the actual file path, the command will look like this.
adb pull "/sdcard/Downloads/video.mp4" D:\Downloads
7. Install/Uninstall apps
In addition to moving files back and forth between your computer and phone, you can actually install an apk file with just a single command. To install an app, you have to specify the full path of the apk file. So replace “path/to/file.apk” with the actual apk file path.
adb install "path/to/file.apk"
If you have multiple devices attached to your computer and want to install the apk file on only one device then use the command below. Replace [serial-number] with the actual device serial number. You can get the device serial number using the fourth command above.
adb -s [serial-number] install "path/to/file.apk"
To uninstall an app, simply execute the command below. Replace with the actual fully qualified package name of the app.
adb uninstall
8. Backup Android Device
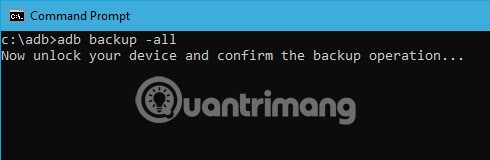
To backup all the device data and applications, users can use the command below. When executed, it will trigger the backup feature, ask the user to accept the action on the Android device, and then create a “backup.adb” file in the current directory.
adb backup -all
9. Restore Android Device
To restore a backup, use the command below. Don’t forget to replace “path/to/backup.adb” with the actual file path.
adb restore "path/to/backup.adb"
10. Reboot Android device into Recovery mode
Recovery mode helps users to repair or restore their Android device using the built-in tools. Generally, users can boot into Recovery mode by using the combination of 2 volume and power buttons. Additionally, users can also connect the device to the system and use the command below to boot into Recovery mode.
adb reboot-recovery
11. Reboot Android device into Bootloader mode
The command below allows the user to boot into bootloader mode. In general, bootloader mode is very similar to fastboot mode.
adb reboot-bootloader
12. Reboot Android device into Fastboot mode
Fastboot mode is commonly used to flash custom ROMs , bootloaders, and even kernels. Use the command below to boot into fastboot mode.
adb fastboot
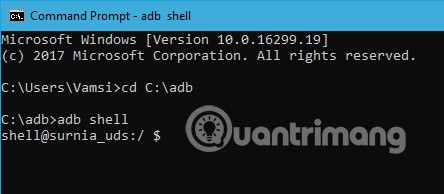
13. Start a Remote Shell
This command starts a remote shell, as well as allowing the user to control and configure the device using shell commands.
adb shell
14. Take a screenshot
Taking a screenshot on Android is not difficult . All you have to do is press the power button and the volume down button at the same time. Alternatively, you can also use this command to take a quick screenshot. Replace “/path/to/screenshot.png” with the actual destination path. If you want, you can customize the file name by changing “screenshot” to whatever you want.
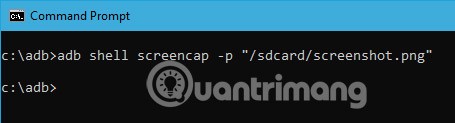
adb shell screencap -p "/path/to/screenshot.png"
When replacing the destination path, the command will look like this.
adb shell screencap -p "/sdcard/screenshot.png"
15. Android Screen Recording
In addition to taking screenshots, users can also record the screen of their Android device using the command below. Again, replace “/path/to/record.mp4” with the actual destination path. Of course, users can customize the file name by changing “record” to whatever name they want.
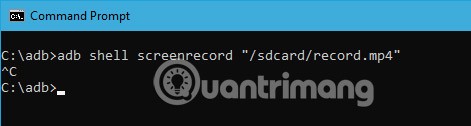
adb shell screenrecord "/path/to/record.mp4"
16. Restart ADB in USB mode
If the ADB server is already started and for some reason the commands still don't work. You can try restarting ADB on USB. There is no standalone command to restart ADB. But the following command will reset the ADB connection over USB. This will cause the ADB server to restart.
adb usb
17. ADB Version
This is a very handy command because very few commands work with the latest versions of ADB. For example, older versions of ADB do not allow you to run the flashall command. So when you get a command error, the first step is to check the adb version. Then you can verify whether the command is supported in that version. Here is the command to check the adb version.
adb version
18. Connect ADB via WiFi
In recent versions of ADB, you can connect directly to any Android device over WiFi. All you have to do is enable USB debugging on the other device and run the following command.
adb connect địa-chỉ-ip
So the command would look like this:
adb connect 192.168.1.104
19. List files
To copy or send a file, you need to know the exact location of the folder. Normally, the phone’s internal memory is named sdcard. So, all the folders inside the phone are located in the /sdcard folder. However, if you want to know the exact location or locate a specific file, you can use the “ls” command. The ls command lists the files in the folder.
adb shell ls "directory_name"
20. List all installed packages
Now uninstalling the packages will require you to get the exact package name. The actual package name is different from the installed app name. So below is the adb command to list all the installed packages.
adb shell pm list packages
Now, the output is quite large. So if you want to list a specific application package, you can try filtering by application name. For example, if you want to search for the package name for FDroid, use the following command.
adb shell pm list packages | findstr "fdroid"
21. List connected Fastboot devices
This is one of the lesser known commands. When you boot your device in Fastboot mode, to check if the device is connected or not, you can use the following command.
fastboot devices
Those are all the basic commands WebTech360 wants to share with readers. If you want to share your thoughts and experiences about using adb commands on Android devices, leave your comments in the comment section below!
Good luck!