Bit is the abbreviation of Binary Digit , which is the basic unit used to measure the amount of information in a computer, calculate the capacity of memory such as: hard drive, USB, memory card, RAM... Bit is the term for the smallest part of computer memory that can store one of two information states: 0 or 1 (can be understood as the on or off state of the transistor in the computer). To better understand the basic units of measurement in computers, please refer to the article below.
Normally on computers, the units used are: Byte, Kilobyte, Megabyte, Gigabyte, Terabyte . The remaining units are rarely used or even not used because they are too large or too small.
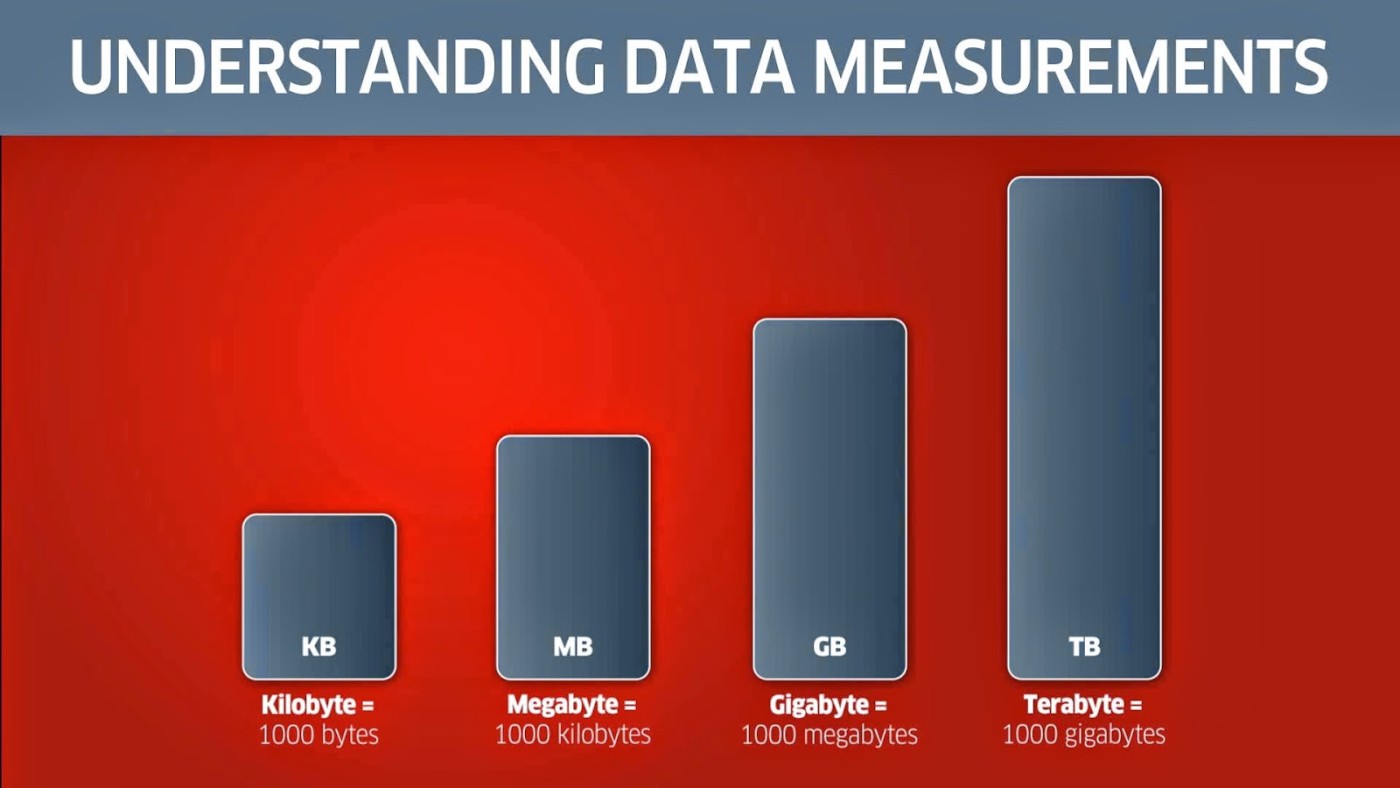
Megabyte (MB), Gigabyte (GB), Terabyte (TB),... are terms used in the computer industry to describe disk space, data storage space, and system memory. A few years ago, we often described hard disk space using the term MB, but now, GB and TB are the most commonly used terms when talking about hard disk capacity. So what are they? It's hard to say exactly what these terms are, because there are different definitions of them in the industry.
- According to the IBM Computer Dictionary, when used to describe the storage capacity of a disk drive, 1MB is 1,000,000 bytes in decimal notation. But when using MB for physical storage, virtual storage, and channel capacity, 2^20 or 1,048,576 bytes is correct.
- According to Microsoft's computer dictionary, 1 MB is equivalent to 1,000,000 bytes or 1,048,576 bytes.
- According to The New Hacker's dictionary, 1 MB is always 1,048,576 bytes, based on the argument that bytes should be counted to powers of 2.
So which definition do we usually use?
When referring to a MB for disk storage, hard drive manufacturers use the standard 1 MB = 1,000,000 bytes. This means that when you buy a 250 GB hard drive, you will get a total of 250,000,000,000 bytes of storage. This number is confusing, because Windows uses the 1,048,576 byte standard, so you will see that a 250 GB hard drive only has 232 GB of available storage, a 750 GB drive will only have 698 GB available, and a 1 TB drive will only have 931 GB. Do you get the idea?
Since all three definitions are accepted, in this article Quantrimang.com will try to help readers approach in the simplest way. 1000 can be replaced by 1024 and still be correct if using acceptable standards. Both standards are correct, depending on the type of storage you are referring to.
Hard drive capacity, memory (HDD, SSD, RAM...)
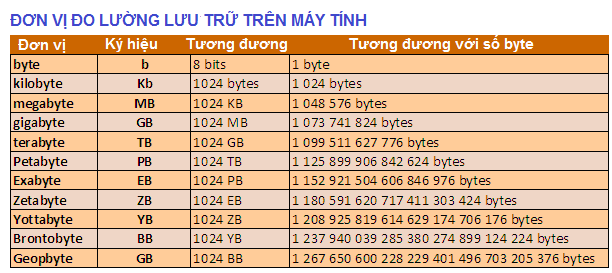
- 1024B (Bytes) = 1KB (Kilobytes)
- 1024KB (Kilobytes) = 1MB (Megabytes)
- 1024MB (Megabytes) = 1GB (Gigabytes)
- 1024GB (Gigabytes) = 1TB (Terabytes)
- 1024TB (Terabytes) = 1PB (Petabytes)
- 1024PB (Petabytes) = 1EB (Exabytes)
- 1024EB (Exabytes) = 1ZB (Zettabytes)
- 1024ZB (Zettabytes) = 1YB (Yottabytes)
- 1024YB (Yottabytes) = 1BB (Brontobytes)
- 1024BB (Brontobytes) = 1GeB (Geopbytes)
Disk Storage
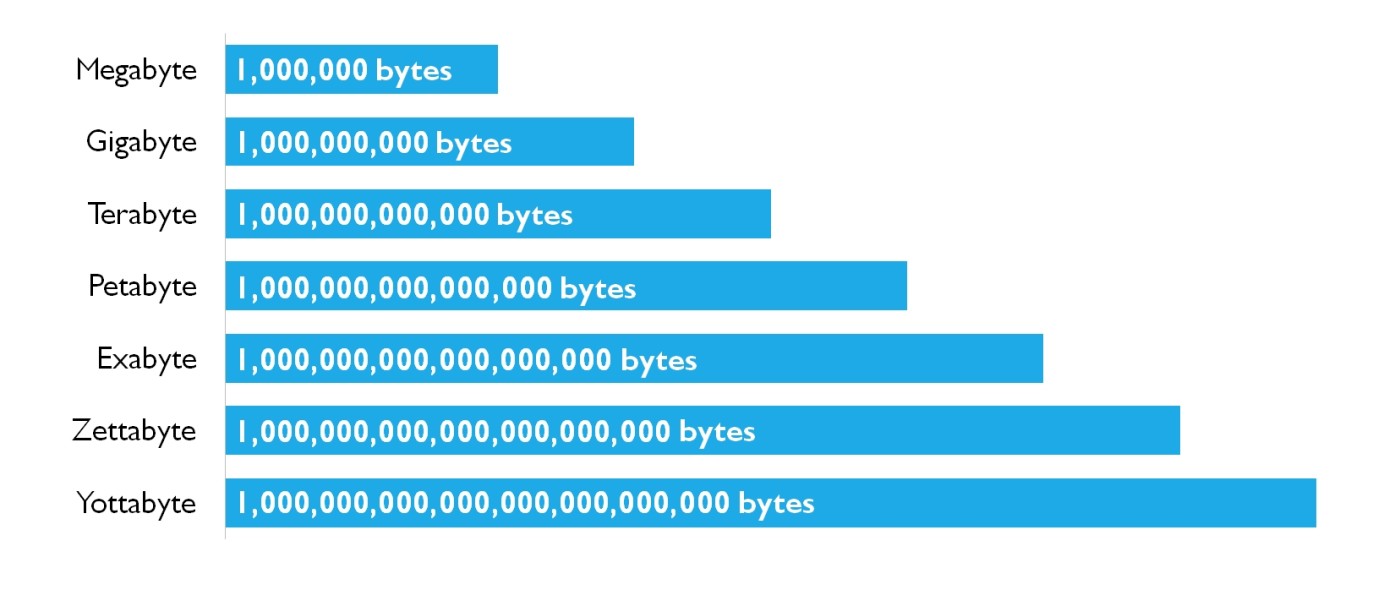
- 1000B (Bytes) = 1KB (Kilobytes)
- 1000KB (Kilobytes) = 1MB (Megabytes)
- 1000MB (Megabytes) = 1GB (Gigabytes)
- 1000GB (Gigabytes) = 1TB (Terabytes)
- 1000TB (Terabytes) = 1PB (Petabytes)
- 1000PB (Petabytes) = 1EB (Exabytes)
- 1000EB (Exabytes) = 1ZB (Zettabytes)
- 1000ZB (Zettabytes) = 1YB (Yottabytes)
- 1000YB (Yottabytes) = 1BB (Brontobytes)
- 1000BB (Brontobytes) = 1GeB (Geopbytes)
Definition of basic units of measurement in computers
Here is a detailed definition of the basic units of measurement in computers:
1. Bit
A bit is the smallest unit of computer memory that can store one of two states: Yes or No. The state is represented by a single binary value, usually 0 or 1. However, the state can also be represented by yes/no, on/off, or true/false. Bits are stored in memory through the use of capacitors that contain an electrical charge. The charge determines the state of each bit, which in turn determines the value of the bit.
Although computers can examine and manipulate data at the bit level, most systems process and store data in bytes. A byte is a string of 8 bits that are considered a unit. Computer memory references are always in bytes. For example, a device that can store 1 terabyte (TB) of data is equivalent to 1,000,000 megabytes (MB). 1MB is 1 million bytes, or 8 million bits. That means a 1TB drive can store 8 trillion bits of data.
Each bit in a byte is assigned a specific value, called a positional value. The positional values of a byte are used to determine the meaning of the entire byte, based on the individual bits. In other words, byte values indicate which character is associated with that byte.
Position values are assigned to each bit in order from right to left, starting with 1 and increasing in value by doubling that value for each bit, as described in this table.
| Bit position (right to left) |
Position value |
|
Bit 1
|
1
|
|
Bit 2
|
2
|
|
Bit 3
|
4
|
|
Bit 4
|
8
|
|
Bit 5
|
16
|
|
Bit 6
|
32
|
|
Bit 7
|
64
|
|
Bit 8
|
128
|
Positional values are used together with bit values to obtain the overall meaning of the byte. To calculate this value, the positional values associated with each 1 bit are added together. This sum corresponds to a character in the applicable character set. A single byte can support up to 256 characters, starting with byte 00000000 and ending with byte 11111111. Different combinations of bit patterns provide a range from 0 to 255, meaning that each byte can support up to 256 bit patterns.
2. Bytes
1 Byte is equivalent to 8 Bits. 1 Byte can represent 256 states of information, for example numbers or numbers combined with letters. 1 Byte can represent only one character. 10 Bytes can represent one word. 100 Bytes can represent a sentence of average length.
3. Kilobyte
1 Kilobyte is approximately 1,000 Bytes , however by definition 1 Kilobyte is equivalent to 1024 Bytes . 1 Kilobyte is equivalent to a short paragraph, 100 Kilobytes are equivalent to 1 A4 page.
4. Megabyte: 1 Megabyte is approximately 1,000 Kilobytes . When computers first came out, 1 Megabyte was considered an incredibly large amount of data. Today, on a computer with a hard drive of 500 Gigabytes is normal, so a Megabyte means nothing.
A 3-1/2 inch floppy disk could hold 1.44 Megabytes or about the size of a small book. 100 Megabytes could hold several Encyclopedias . A CD-ROM drive had a capacity of 600 Megabytes.
5. Gigabyte
1 Gigabyte is approximately 1,000 Megabytes . 1 Gigabyte is a fairly common term used today when referring to disk space or storage. A Gigabyte is a large amount of data, roughly twice the amount of data that a CD-ROM can store. But only about 1,000 times the capacity of a 3-1/2 inch floppy disk. 1 Gigabyte can store the content of a book that is about 10 meters long when stacked on a shelf. 100 Gigabytes can store the content of a whole floor of a library.
6. Terabyte
1 Terabyte is approximately one trillion (quadrillion) bytes or 1,000 Gigabytes . This is so large that it is not yet a common term. 1 Terabyte can store about 3.6 million 300 Kilobyte photos or about 300 hours of good quality video. 1 Terabyte can store 1,000 copies of the Encyclopedia Britannica . 10 Terabytes can store an entire library. That's a lot of data.
7. Petabyte
1 Petabyte is approximately 1,000 Terabytes or one million Gigabytes . It is hard to imagine the amount of data that a Petabyte can store. 1 Petabyte can store about 20 million 4-door filing cabinets full of documents. It can store 500 billion pages of standard-sized printed text. That amount of data would require about 500 million floppy disks to store.
8. Exabyte
1 Exabyte is approximately 1000 Petabytes . In other words, 1 Petabyte is approximately 10 to the 18th power bytes or 1 billion Gigabytes . It is very difficult to compare an Exabyte . It is said that 5 Exabytes contain an amount of words equivalent to the entire vocabulary of all mankind.
9. Zettabyte
1 Zettabyte is approximately 1,000 Extabytes . There is nothing comparable to 1 Zettabyte but to represent it would require a lot of 1s and 0s.
10. Yottabyte
1 Zottabyte is approximately 1,000 Zettabytes . There is nothing comparable to 1 Yottabyte.
11. Brontobyte
1 Brontobyte is approximately 1,000 Zottabytes . The only thing that can be said about the size of 1 Brontobyte is that there are 27 zeros after the 1!
12. Geobyte
1 Geopbyte is approximately 1,000 Brontobytes. I wonder if we will ever see a 1 Geopbyte hard drive in our lifetime, because 1 Geopbyte is equivalent to 152,676,504,600,228,322,940,124,967,031,205,376 bytes! (size: 152 million 676 thousand 504 billion billion billion bytes (not sure if I read it correctly @@)).
CPU speed
CPU speed, also known as Clock Speed, is a measure of the power of a CPU. Generally speaking, a higher clock speed means a faster CPU.
The CPU in your computer processes many instructions (low-level calculations like arithmetic) from different programs every second. Clock speed measures the number of cycles your CPU performs per second, measured in GHz (gigahertz).
A machine cycle is technically a pulse synchronized by an internal oscillator, but for us it is a basic unit for understanding the speed of a CPU. During each cycle, billions of transistors in a microprocessor are turned on or off.
For example, a CPU with a clock speed of 3.2 GHz performs 3.2 billion cycles per second. In the past, when CPUs were not as fast as they are now, the units of measurement were megahertz (MHz), kiloherz (kHz)...
Before the advent of multi-core CPUs, clock speed was considered the primary parameter for comparing single-core processors. Today, it is considered along with other parameters such as core count, CPU cache, and power consumption.
Bus
In computing, bus is an abbreviation of "omnibus", which refers to a system of communication and data transfer between hardware components.
The memory bus is made up of three components: the data bus, the address bus, and the control bus. In addition, RAM also has its own bus.
- The data bus is responsible for transferring information between the memory and the chipset. The larger the data bus, the higher the performance of the machine because it can allow more data to pass through in the same amount of time, this is called data bandwidth.
- The address bus communicates with the system where specific information can be located or stored as data enters or leaves memory.
- The control bus carries instructions from the CPU and returns status signals from devices.
- RAM bus or RAM bus is the unit that represents the size of the data transmission channel inside RAM, the larger the RAM bus, the more data is processed.
From the RAM bus we can calculate the bandwidth of RAM using the formula: Bandwith = (bus speed x bus width)/8.
In addition, depending on the RAM generation (identified by DDR symbols), the RAM bus will be different, usually increasing with the RAM generation. This means that the newer the RAM generation, the higher the RAM bus. You can see the details below:
SDR SDRAM:
- PC-66: 66MHz bus
- PC-100: 100MHz bus
- PC-133: 133MHz bus
DDR SDRAM:
- DDR-200: also known as PC-1600. 100MHz bus with 1600MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR-266: also known as PC-2100. 133MHz bus with 2100MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR-333: also known as PC-2700. 166MHz bus with 2667MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR-400: also known as PC-3200. 200MHz bus with 3200MB/s bandwidth.
DDR2 SDRAM:
- DDR2-400: also known as PC2-3200. 100MHz clock, 200MHz bus with 3200MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR2-533: also known as PC2-4200. 133MHz clock, 266MHz bus with 4267MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR2-667: also known as PC2-5300. 166MHz clock, 333MHz bus with 5333MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR2-800: also known as PC2-6400. 200MHz clock, 400MHz bus with 6400MB/s bandwidth.
DDR3 SDRAM:
- DDR3-1066: also known as PC3-8500. 533MHz clock, 1066MHz bus with 8528MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR3-1333: also known as PC3-10600. 667MHz clock, 1333MHz bus with 10664MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR3-1600: also known as PC3-12800. 800MHz clock, 1600MHz bus with 12800MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR3-2133: also known as PC3-17000. 1066MHz clock, 2133MHz bus with 17064MB/s bandwidth.
DDR4 SDRAM:
- DDR4-2133: also known as PC4-17000. 1067MHz clock, 2133MHz bus with 17064MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR4-2400: also known as PC4-19200. 1200MHz clock, 2400MHz bus with 19200MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR4-2666: also known as PC4-21300. 1333MHz clock, 2666MHz bus with 21328MB/s bandwidth.
- DDR4-3200: also known as PC4-25600. 1600MHz clock, 3200MHz bus with 25600MB/s bandwidth.
Now you have a pretty good understanding of computer units of measurement, right?
Have fun!
See also: