If you often wander on websites or Smartphone Forums, you must have seen topics related to rooting devices, especially Android devices. If you are wondering why you need to root or how to root your Android device. Please refer to the article below by WebTech360.
Once you root your Android phone, you have full system access and can run a variety of apps that require root access. These apps can disable bloatware, control allowed apps, enable connectivity, and many other great things.
Android Root Overview
1. What is Root?
Rooting has many meanings depending on the device and the situation. When using Android root, here rooting is unlocking the Android device to allow more access to the core software that may have been blocked by the device manufacturer.
Android is developed on the Linux platform. For Linux and other UNIX operating systems, the root user is equivalent to the Administrator user on Windows. The root user has access to the entire file system in the operating system and can do whatever he wants. By default, the user will not have administrative rights on the Android device and certain applications will not work without administrative rights. Some settings and deep intervention into the system will also require rooting the device to be able to perform. In other words, Root Android is a way for you to gain administrative rights on the Android device, from which you can perform advanced tweaks or deep intervention into the system files.
With administrator rights, you can disable bloatware on your phone, manually disallow apps, run a firewall, access the entire file system, or connect to the device, even when tethering is disabled. Many apps in the Google Play store (formerly the Android Market) require administrator rights and won't work until you root your device.
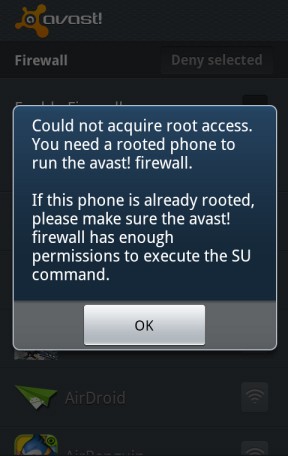
Rooting the device is not required. We only need to root the device if we want to do things that require user administrative rights.
2. Why should you root your Android device?
Here are some reasons why you should root your Android device:
- Install Custom ROM:
Once your Android device is rooted, you can Flash a Custom ROM or Kernel, which means you will experience and use your Android phone exactly like you just bought it.
- Remove Preinstalled Crapware:
Manufacturers do not allow users to uninstall Preinstalled applications on their devices. However, when rooting these devices, users can uninstall the settings easily.
- Block ads on any application:
Every time you play a game,... a popup ad appears on the screen and this makes you feel extremely uncomfortable. However, if a device has been rooted, all these ads will be "removed" and will no longer annoy you.
- Installing incompatible applications:
Some apps require root access to be installed on your device. So if your device is rooted, you can freely install these apps.
- Speed up Android device boot process and extend battery life:
Some apps like Greenify can automatically close unused apps on your Android device to improve your device performance. And of course, Greenify needs root access.
- Update to the latest Android version:
Updating the operating system is always a headache for Android users. By rooting your device, you can always download and install the latest operating system (optimized for each device model) before it is officially available.
3. Method to root Android phone
There are several ways to root an Android phone, and the one you use depends on your phone. Generally, rooting involves one of the following processes:

-
Unlocking the Bootloader: Google and device manufacturers do not officially support rooting, but they do provide an official way to gain low-level access to some devices, which then allows you to root. For example, Nexus devices are for developers and you can easily unlock the bootloader with a single command. You can then root the device by flashing the zip file containing the SU binary from the recovery screen. Other manufacturers also provide ways to unlock the bootloader, but only for certain devices.
-
Exploits : Some manufacturers don’t provide an official way to unlock their bootloaders and modify their software. However, you can still root these devices by exploiting a security vulnerability on the device to install the SU binary to the system partition. An OTA update can fix the vulnerability and unroot the device. For example, there is an $18,000 bounty for the first person to root a Samsung Galaxy S5 running on Verizon or AT&T. And a vulnerability has been found, but future updates may prevent it from working and remove the ability to root the Galaxy S5.
- Flashing CyanogenMod or a Custom ROM : Technically, this is an extension of the above two methods. Unlocking the bootloader and exploiting a security vulnerability can allow you to flash a custom ROM like CyanogenMod, which is often pre-rooted. CyanogenMod has a simple toggle on its settings screen that allows you to enable or disable root access. Upgrading to a new version of CyanogenMod or a custom ROM will not unroot your device if the ROM comes with a built-in way to enable root.
4. Some notes before rooting Android phone
Before rooting your Android phone or tablet, there are a few things users should know:
- Warranty : Many manufacturers claim that rooting voids the device’s warranty. However, rooting Android does not actually harm the hardware. Users can “unroot” the device and the manufacturer will have no way of knowing if the device has ever been rooted.
- Security : Specifically, Google Wallet has a vulnerability on rooted devices that could allow other apps to access the user’s PIN and other personal information. Google Wallet will display a warning message if the user is using the program on a rooted device. If you are one of those people who uses Google Wallet to make NFC payments, you may want to reconsider rooting your device.
- “Bricking” : Rooting a device is a safe process. However, there is always some risk of harming the device if the user changes the normal parameters and performs hacks on the device. Especially if the user is trying to root a device or an operating system version that is not supported by a tool. “Bricking” is damaging the device, making it no different from the function of a brick. When rooting, jailbreaking, installing a custom ROM, or hacking around, there are always certain risks. It is better to do a little research first and see if anyone else has reported successfully rooting the same device as you.
5. How to root Android phone using SuperSU
Before starting this process, you will need to unlock the bootloader the official way and then install the TWRP Recovery environment , then use TWRP to root the phone.
Next, to get root access, we’ll use a program called SuperSU, which gives us access to other apps. While you can download SuperSU from the Google Play Store, that version doesn’t actually give us root access. Luckily, SuperSU has a .zip file that you can flash with TWRP, which gives us root access along with SuperSU’s Android app management features.
To get started, head over to the link below to download the latest version of SuperSU as a .zip file to your computer. Then plug your phone into your computer using a USB cable and drag the SuperSU zip file to your phone’s internal storage or SD card.
http://forum.xda-developers.com/showthread.php?t=1538053
Next, boot your phone into TWRP recovery. How to access this mode varies depending on your phone. For example, you need to press the power button and the volume down button at the same time, then use the volume keys to boot into Recovery Mode .
Once in this mode, you will see the familiar TWRP main screen, click on the Install button .
Note: It is recommended that you take a backup in TWRP before proceeding.
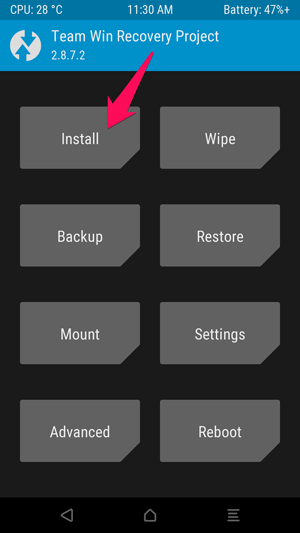
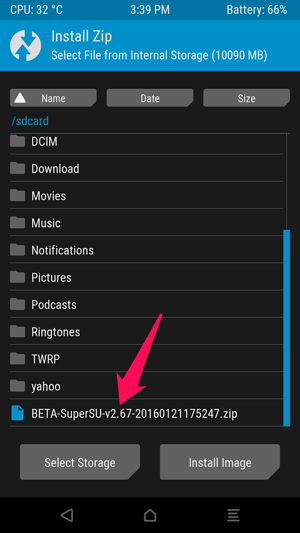
You will see a screen like the one below appear, scroll down and navigate to the SuperSU ZIP file you transferred earlier.
Tap on SuperSU zip and you will see this screen, swipe to confirm flash.
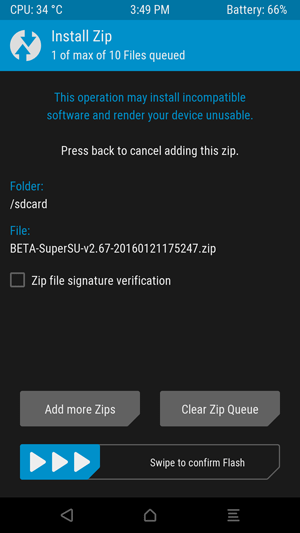
Flashing the SuperSU package will only take a few minutes. Once it's finished, tap the Wipe cache/Dalvik button that appears and swipe to confirm.
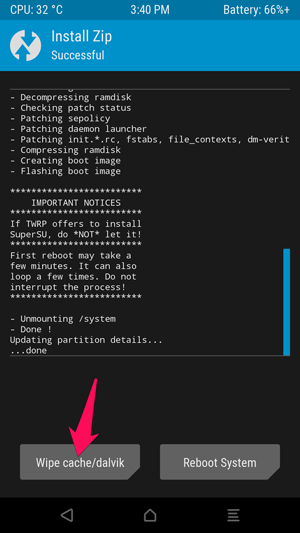
When finished, tap the Reboot System button to reboot into Android.
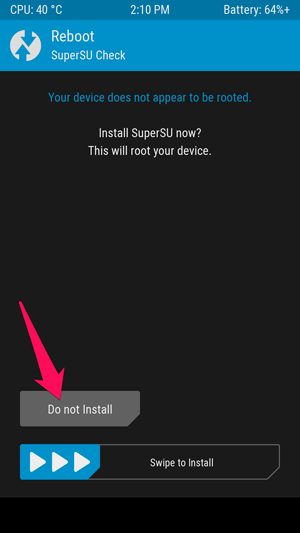
If TWRP asks if you want to install SuperSU now, select Do Not Install . Sometimes TWRP can't detect that you already have SuperSU on your device, so it will ask to flash its built-in version. But it's best to flash the latest version of SuperSU yourself as you did.
Manage root permissions with SuperSU app
When you reboot your phone, you’ll see a new SuperSU icon in your app drawer. SuperSU controls which other apps on your phone have root access. Whenever an app wants to request root access, it has to ask the SuperSU app, which will display a prompt asking for it.
To make sure rooting is working properly, you can download the Root Checker app and verify your root status. Or download a root-only app that you want to try and see if it asks you for root permissions.
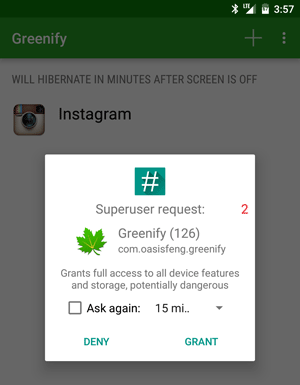
For example, if you open the Greenify app, a handy Android battery saver app for rooted phones, you will see a notification like the one below asking for root access. If you click Grant and get a success message, this means you have successfully rooted your phone.
To manage root permissions, open the app drawer and tap the SuperSU icon. You'll see a list of apps that have been granted or denied root permissions. Tap an app to change its permissions. If you want to unroot, open the SuperSU app, go to its Settings screen , and tap the Full unroot option .
6. Use KingRoot to root any Android phone
Requirements: Your Android device must have at least 20% battery or more to avoid interruption during rooting process.
Steps to follow:
Step 1:
On your Android device, open Settings => Security => Device Administration => check Unknown Source to enable.
Step 2:
Download and install KingRoot APK application on your Android device.
https://androidmtk.com/download-kingroot-application
Step 3:
Once the installation is complete, you will see the app icon on the Launcher Menu.
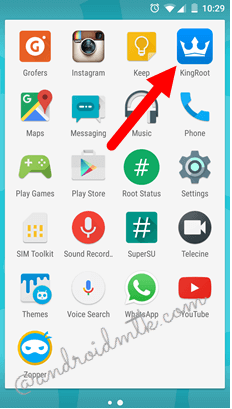
Step 4:
Click on KingRoot icon to open the application.
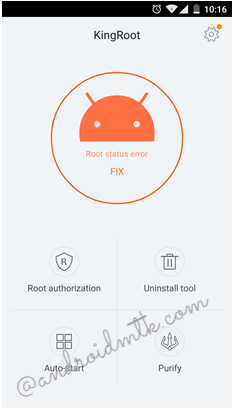
Step 5:
Next, click the Start Root button to begin the rooting process.
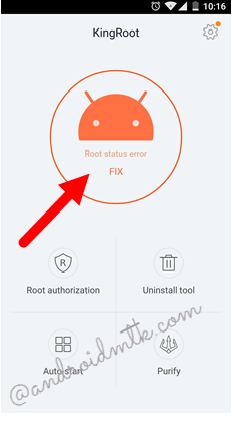
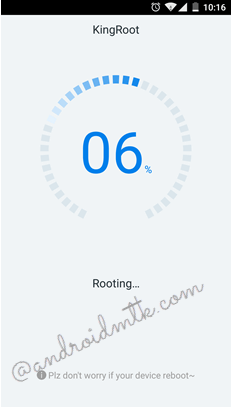
Step 6:
KingRoot will now start the process of rooting your Android device.
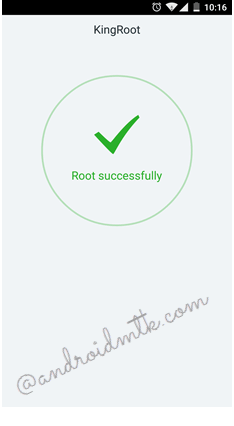
Step 7:
Wait until a large green check mark appears on your Android device screen as shown below, which means your device has been successfully rooted.
Step 8:
Restart your Android device and you're done.
In addition, you can refer to the video instructions for rooting Android 4.3, 4.4, 5.0 and 5.1 devices below:
See more articles below:
Good luck!