How to read the index on a blood pressure monitor accurately helps you understand the parameters on the monitor, helping patients with blood pressure problems to monitor this index every day.
Table of Contents
What is blood pressure index? Classification of measurement indicators
Blood pressure is a measurement of the pressure of blood in the arteries when the heart contracts and when the heart relaxes.
There are 2 types of blood pressure measurements:
- Systolic blood pressure (symbolized by SYS): The largest blood pressure reading when measured represents the pressure of blood on the arteries when the heart is contracting. This number is usually located at the top of the blood pressure monitor.
- Diastolic blood pressure (symbolized by DIA): The lowest blood pressure number when measured, representing the pressure of blood in the arteries when the heart relaxes. This index is usually located at the bottom.
The unit of blood pressure measurement is millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
What is normal blood pressure?
Normal blood pressure ranges from about 90/60 mmHg to 140/90 mmHg. In particular, blood pressure in young people can reach 145/95 mmHg.
High blood pressure is when the systolic blood pressure is greater than 140 and the diastolic blood pressure is greater than 90.
Low blood pressure is when the diastolic blood pressure is less than or equal to 90 and the systolic blood pressure is less than 60.
Note: To determine whether a person has high blood pressure or not, it is necessary to measure many times a day such as morning, noon, afternoon and evening, and must measure in both arms after 5 minutes of resting, or after at least 1 - 2 minutes in a standing position.
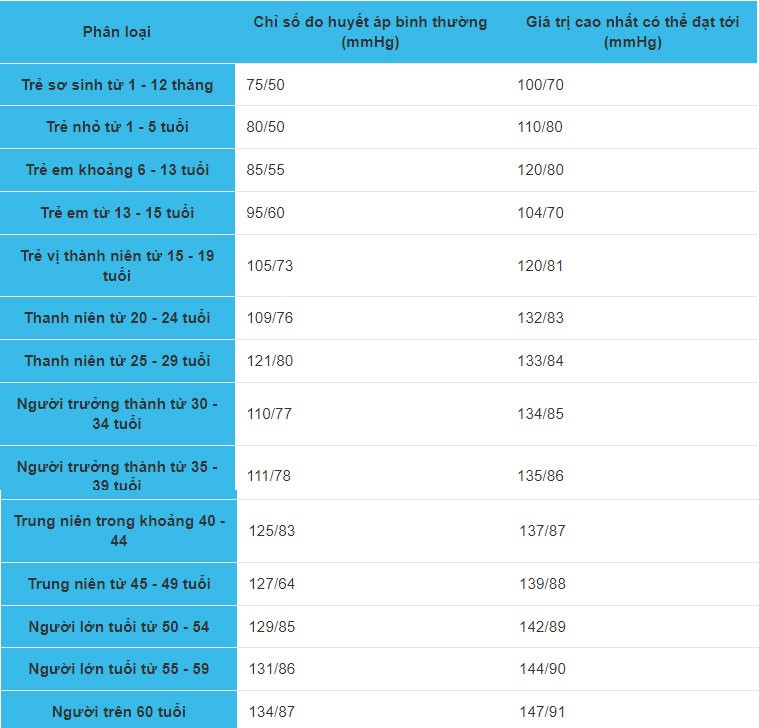
Below is a table of blood pressure levels and normal blood pressure by age.
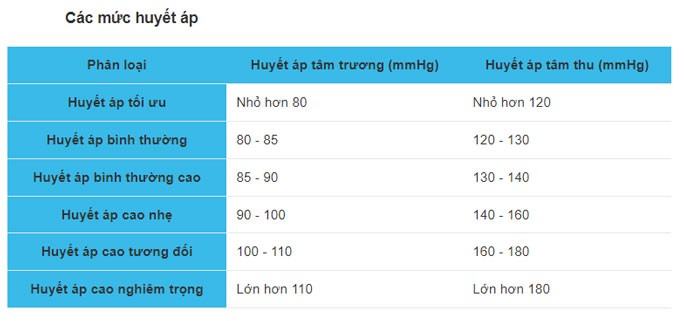
Normal blood pressure by age