What is a meteor? Why does a meteor occur? Let's find out together!
As a comet passes close to the Sun, it heats up and some of the comet vaporizes. After the comet has circled the Sun many times, many small pieces of the comet are left behind along the comet's path. Meteor showers occur when Earth passes through the comet's path. When this happens, fragments of the comet, most of which are no larger than a grain of sand, create bright streaks of light in the night sky as they burn up in Earth's atmosphere. The fragments that enter Earth's atmosphere are called meteors. On any given night, a few small meteors shooting across the sky are likely to occur. However, during a meteor shower, dozens to hundreds of meteors can be seen per hour. Many of these meteor showers can be predicted and occur at the same time each year.
Let's find out more details and why there are shooting stars!
Why are there shooting stars?
When moving at a speed of about 100,000km/h, the air molecules in the path of the meteorite are heated by the shock wave, or compressed so strongly that the temperature of the shock wave increases to thousands of degrees and causes the material components of the meteorite to become incandescent.

In fact, comets are the cause of meteor showers. Comets are celestial bodies orbiting the Sun made of ice, dust, and rock. When moving close to the Sun, comets break up, creating dust trails in their orbit.
If comets pass through or are near the Earth's orbit, and the Earth moves close to that intersection, the comet's dust and gas will be thrown into the atmosphere, causing a lot of shooting stars. At that time, they are called Meteor Showers.
The nodes are defined on the path of the Earth and each year the Earth will pass through the nodes at a certain time. Therefore, meteor showers have a cycle of 1 year.
Famous Meteor Showers
- Quadrantids: January 1 to 5 every year. Peak usually January 3 – 4.
- η-Aquariids: From April 19 to May 28 every year. Peak on May 5-6.
- Perseids: July 17 to August 24. Peaks August 12-13.
- Orionids: October 2-7. Peaks October 4-5.
- Leonids: November 10-23. Peaks November 16-17.
- Geminids: December 7-17. Peaks December 12-13.
The peak times of meteor showers change every year. Only when the shower is near do we know the exact times.
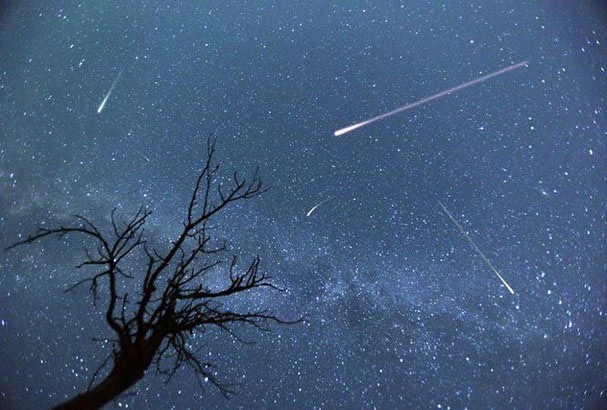

How to watch meteor shower
To see a perfect meteor shower, you must determine the direction of the constellations.
Wherever you can see those constellations, you can see meteor showers, so we have to determine the direction of the constellations to be able to see a perfect meteor shower.
The closer a place is to the equator, the easier it is to observe meteor showers. Fortunately, Vietnam is located near the equator, so it is quite convenient to observe meteor showers.
What is the difference between meteor, shooting star and meteorite?
Meteorites : These rocks are still in space. Meteorites range in size from dust grains to small asteroids.
Meteor : When meteors enter the Earth's atmosphere (or that of another planet, such as Mars) at high speed and burn up, the resulting fireballs or "shooting stars" are called meteors.
Meteorite : When a meteorite survives the trip through the atmosphere and hits the ground, it is called a meteorite.