Analyzing an Attack (Part 3)
In part 2 of this series, we have left all the necessary information required for an attack on the victim's network.
Don Parker
This series will be based on a network vulnerability. What will be introduced in the article is a real attack, starting from reconnaissance to enumeration, exploiting network services and ending with notification exploitation strategies.
All of these steps will be viewed at the packet level, and then explained in detail. Being able to view and understand an attack at the packet level is extremely important for both sys admins and network security personnel. The output of firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and other security devices will always be used to see the actual network traffic. If you don’t understand what you are seeing at the packet level, all of your network security technology is useless.
The tools used for simulating a cyber attack are:
IPEye
TFTP client
FU Rootkit
Setup Step
There are many scanning operations on the Internet today, not to mention the operations of worms and other forms of malware such as viruses. All of these will be harmless noise to a well-protected computer network. What we should consider is someone who is deliberately targeting a computer network. This article will assume that the attacker has already attacked his victim and has done some research beforehand such as finding out the IP address and network addresses of the victim. The attacker may also have tried to exploit information such as email addresses associated with that network. This type of information is very important in case the attacker has found but has no way to get into the network after scanning, enumerating and spoofing it. The email addresses he has collected will be useful in setting up a client-side attack by trying and inviting the user to a malicious website through a link in an email. These types of attacks will be covered in later articles.
How it works
We should observe the actions of a hacker as he scans and enumerates the victim network. The first tool that the hacker uses is Nmap. Although Nmap has few IDS signatures, it is still a very useful and widely used tool.
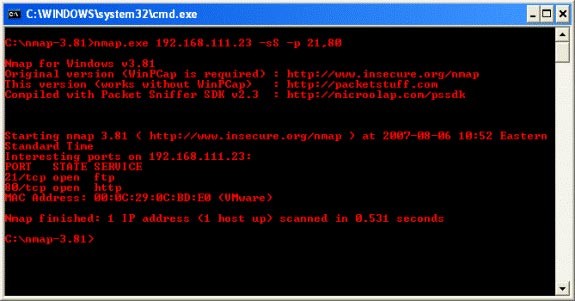
We can see through the syntax used by the hacker in the screenshot above, the hacker has chosen ports 21 and 80 because he has some exploits that can be used through the Metasploit Framework. Not only that but also the two system services and protocols that he understands quite well. It is clearly shown that he is using a SYN scan, which is the most commonly used type of port scan. This is also due to the fact that when a TCP service listening on a port receives a SYN packet, it will send back a SYN/ACK packet. The SYN/ACK packet indicates that a service is indeed listening and waiting for a connection. However the same problem is not the case with UDP, which relies on services like DNS (DNS also uses TCP but it mostly uses UDP for the majority of its transactions).
The syntax listed below is the output that Nmap gathers from the packets it sends, but more accurately from the packets it receives as a result of the SYN scan it performs. We can see that there appear to be FTP and HTTP services provided. We don’t really care about the MAC address so we’ll ignore that. Tools like Nmap don’t often have errors so it’s usually good to verify your information at the packet level to ensure accuracy. Not only that but it also allows you to look at the packets coming back, from the victim network, to glean architectural, service and host information from them. Look up
the packets
There are a number of programs available today that will dig into the packets and find out information like the operating system type, architectural information, such as x86 or SPARC, and more. That's not enough but it's important when we're looking at letting a program do the work for us. With that in mind, let's take a look at the Nmap packet trace and find out some information about the victim network.
10:52:59.062500 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 43, id 8853, offset 0, flags [none], proto: ICMP (1), length: 28) 192.168.111.17 > 192.168.111.23: ICMP echo request seq 38214, length 8
0x0000: 4500 001c 2295 0000 2b01 0dd3 c0a8 6f11 E..."...+.....o.
0x0010: c0a8 6f17 0800 315a 315f 9546 ..o...1Z1_.F
10:52:59.078125 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 128, id 396, offset 0, flags [none], proto: ICMP (1), length: 28) 192.168.111.23 > 192.168.111.17: ICMP echo reply seq 38214, length 8
0x0000: 4500 001c 018c 0000 8001 d9db c0a8 6f17 E.............o.
0x0010: c0a8 6f11 0000 395a 315f 9546 0000 0000 ..o...9Z1_.F....
0x0020: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ..............Shown in the two packets above is the open sequence from Nmap. What it does is send an ICMP echo request to the victim network. You will notice that it is not equipped with a port number, because ICMP does not use ports, but is managed by the ICMP error message generator built into the TCP/IP protocol stack. This ICMP packet is also labeled with a unique number, in this case 38214, so that the TCP/IP stack can examine the return traffic, and associate it with the previous ICMP packet sent. The packet just above is the reply from the victim network, in the form of an ICMP echo reply. The sequence number 38214 is also taken into account. This is how the hacker knows that there is a computer or network behind that IP address.
This open sequence of ICMP packets is why Nmap has an IDS notation for it. The ICMP host discovery option can be disabled in Nmap if desired. What kind of information can be gleaned from the ICMP echo reply packet from the victim network? There is not much information here that can help us understand the network. However, preliminary attacks can be used in areas related to the operating system. The time to reside field and the value next to it are highlighted in the packet above. The value of 128 indicates the fact that this computer is probably a Windows computer. While the ttl value does not tell us exactly what is related to the operating system, it will be the basis for the next packet that we will look at.
Conclusion
In this part one, we looked at a scan of a network in an attack for two specific ports using Nmap. At this point, the attacker knows for sure that there is a computer or a network of computers residing at that IP address. In part 2 of this series, we'll continue our research into this packet's trace, and find out what other pieces of information we can glean.
In part 2 of this series, we have left all the necessary information required for an attack on the victim's network.
We showed you in part one the information that can be observed while opening the packet sequence sent by Nmap. The sequence sent starts with an ICMP echo response to determine if the computer or network has been assigned an IP address.
Tired of Microsoft Teams workflows and Power Automate errors halting your productivity? Get step-by-step solutions to common issues like authentication failures, timeouts, and flow errors. Fix them in minutes and automate effortlessly!
Facing Microsoft Teams "Download Error" on MacBook? Discover proven troubleshooting steps to resolve download failures quickly, from cache clears to reinstalls, and get back to smooth teamwork.
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Where is Teams" Folder Error? Discover proven, step-by-step troubleshooting fixes to resolve it quickly and restore smooth teamwork. Latest methods included!
Frustrated by Microsoft Teams JavaScript Error on desktop app? Discover proven steps to fix it fast: clear cache, update, reset, and reinstall. Get back to seamless collaboration in minutes!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Guest Login" Error? Discover step-by-step fixes, from quick cache clears to admin settings, to resolve guest access issues fast and collaborate seamlessly. Updated with the latest tips!
Tired of the Microsoft Teams "For PC" download error blocking your work? Follow our proven, step-by-step guide to resolve it quickly and get Teams running smoothly on your PC today.
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Windows 7" login error? Discover step-by-step fixes for this frustrating issue on Windows 10/11. Clear cache, edit registry, and more – get back to seamless collaboration today!
Tired of Microsoft Teams Error Code 0x80070005 blocking your meetings? Follow this 2026 guide with step-by-step fixes for access denied issues. Get Teams running smoothly in minutes!
Master the installation of the Microsoft Teams Add-in for Outlook 2026 effortlessly. Boost your productivity with seamless scheduling and meetings. Follow our proven, up-to-date steps for instant success!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "License Error" 2026? Discover proven, step-by-step solutions to resolve it fast. Clear cache, check licenses, and get back to seamless collaboration—no IT help needed!
Whether youre in your 50s, 60s, or even 70s, its not too late to prioritize your health and put yourself first. Here are the best exercises for people 50 and older.
Struggling with Microsoft Teams Error Caa50024 on Windows 10/11? Follow our step-by-step fixes to resolve crashes and launch issues quickly. Latest proven solutions for seamless teamwork.
Stuck with Microsoft Teams login error AADSTS50011? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes to resolve the reply URL mismatch issue and log in seamlessly. No tech skills needed!
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Win 7" Compatibility Error blocking your meetings? Get instant fixes with our step-by-step guide, including workarounds for older Windows versions. Resolve it now and stay connected!
Tired of the endless Microsoft Teams "Error R" restart loop? Get step-by-step fixes to solve Microsoft Teams Error R quickly. Clear cache, reset, reinstall & more for smooth collaboration. Works on Windows, Mac & web.