How to use constants in Golang

What is a Constant or Const in Golang? Here's what you need to know about using constants in Go.
Operators are the foundation of every programming language. Therefore, the functionality of Golang language is incomplete without the use of operators. Operators allow us to perform different types of operations on operands. In Go language, operators can be classified based on their different functions .

Arithmetic operators
These operators are used to perform operations on operands in Go language:
Note: -, +, !, &, *, <- and ^ are also called unary operators and the precedence of unary operators is higher. The ++ and — operators come from statements, they are not expressions, so they lie outside the operator hierarchy.
For example:
//Minh họa chương trình Go dùng toán tử số học
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
p:= 34
q:= 20
// Phép cộng
result1:= p + q
fmt.Printf("Result of p + q = %d", result1)
// Phép trừ
result2:= p - q
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p - q = %d", result2)
// Phép nhân
result3:= p * q
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p * q = %d", result3)
// Division
result4:= p / q
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p / q = %d", result4)
// Modulus
result5:= p % q
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p %% q = %d", result5)
}
Result:
Kết quả của p + q = 54
Kết quả của p - q = 14
Kết quả của p * q = 680
Kết quả của p / q = 1
Kết quả của p % q = 14Relational Operators
Relational operators are used to compare two values. Let's look at each operator one by one:
For example:
// Minh họa chương trình Go dùng toán tử quan hệ
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
p:= 34
q:= 20
// ‘=='(Equal To)
result1:= p == q
fmt.Println(result1)
// ‘!='(Not Equal To)
result2:= p != q
fmt.Println(result2)
// ‘<‘(less than)="" result3:="p">< q="" fmt.println(result3)="" ‘="">'(Greater Than)
result4:= p > q
fmt.Println(result4)
// ‘>='(Greater Than Equal To)
result5:= p >= q
fmt.Println(result5)
// ‘<='(less than="" equal="" to)="" result6:="p"><= q="" fmt.println(result6)="" }="">Result:
false
true
false
true
true
falseLogical operators
They are used to combine two or more conditions/constraints or to supplement the evaluation of the initial condition under consideration.
For example:
// Minh họa chương trình Go dùng toán tử logic
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var p int = 23
var q int = 60
if(p!=q && p<=q){ fmt.println("true")="" }="" if(p!="q" ||=""><=q){ fmt.println("true")="" }="" if(!(p="=q)){" fmt.println("true")="" }="" }="">Result:
True
True
TrueBitwise operators
In Go language, there are 6 bitwise operators that operate on bit level or are used to perform bit-by-bit operations. Following are the bitwise operators:
For example:
// Minh họa chương trình Go dùng toán tử bitwise
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
p:= 34
q:= 20
// & (bitwise AND)
result1:= p & q
fmt.Printf("Result of p & q = %d", result1)
// | (bitwise OR)
result2:= p | q
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p | q = %d", result2)
// ^ (bitwise XOR)
result3:= p ^ q
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p ^ q = %d", result3)
// < (left="" shift)="" result4:="p">< 1="" fmt.printf("\nresult="" of="" p="">< 1="%d" ,"="" result4)="">> (right shift)
result5:= p >> 1
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p >> 1 = %d", result5)
// &^ (AND NOT)
result6:= p &^ q
fmt.Printf("\nResult of p &^ q = %d", result6)
}
Result:
Kết quả của p & q = 0
Kết quả của p | q = 54
Kết quả của p ^ q = 54
Kết quả của p < 1="68" kết="" quả="" của="" p="">> 1 = 17
Kết quả của p &^ q = 34Assignment Operator
Assignment operators are used to assign a value to a variable. The left operand of an assignment operator is a variable and the right operand of an assignment operator is a value. The value on the right must have the same data type as the variable on the left, otherwise the compiler will report an error. The different types of assignment operators are shown below:
For example:
// Minh họa chương trình Go dùng toán tử gán
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var p int = 45
var q int = 50
// “=”(Simple Assignment)
p = q
fmt.Println(p)
// “+=”(Add Assignment)
p += q
fmt.Println(p)
//“-=”(Subtract Assignment)
p-=q
fmt.Println(p)
// “*=”(Multiply Assignment)
p*= q
fmt.Println(p)
// “/=”(Division Assignment)
p /= q
fmt.Println(p)
// “%=”(Modulus Assignment)
p %= q
fmt.Println(p)
}
Result:
50
100
50
2500
50
0Other operators
// Minh họa chương trình sử dụng toán tử khác
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
a := 4
// Dùng địa chỉ của toán tử (&) toán tử trỏ gián tiếp (*)
b := &a
fmt.Println(*b)
*b = 7
fmt.Println(a)
}
Result:
4
7What is a Constant or Const in Golang? Here's what you need to know about using constants in Go.
Variadic functions in Go allow you to pass a variable number of arguments to a function. Here's everything you need to know about variadic functions in Golang.
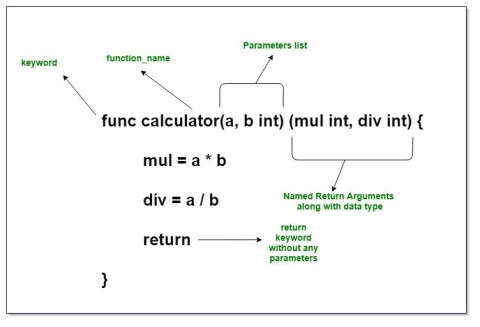
In Golang, named return parameters are often referred to as named parameters. Golang allows naming the return parameters or results of functions in the function signature or definition.
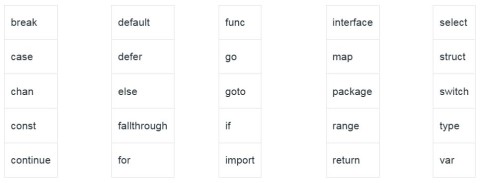
Keyword - Keywords are words in a language that are used for some internal processes or represent some predefined actions. Here is what you need to know about keywords in Golang.
Data types specify what type of data a valid Go variable can hold. In the Go language, types are divided into four categories as follows:
Go supports two main ways to pass arguments: Pass by Value and Pass by Reference. Go uses pass by value by default.
In Go language, you are allowed to return multiple values from a function, using the return statement. In other words, in a function, a return statement can return multiple values.
Golang like most other programming languages has switch statement. Here is how to use switch statement in Golang.
In this article, we will learn how to use default case to avoid deadlock. But first, we will learn what is deadlock case when using select command in Golang?
Anonymous structs in Golang are temporary structures with no names used for one-time purposes, while anonymous fields allow embedding of unnamed fields.
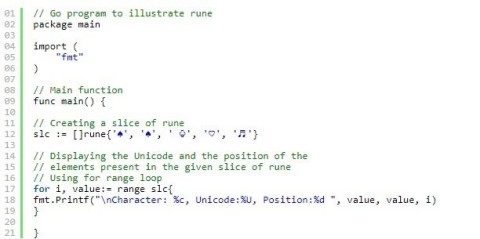
What is Rune in Golang? How to use Rune in Golang? This article will give you the answer.
_(underscore) in Golang is called Blank Identifier. Identifier is a user-defined name of program elements used for identification purposes.
Hello, World! is the first basic program in any programming language. You can write this first program in Golang by following the steps below.
Golang can be easily installed on Windows. Here is a step-by-step guide to install Golang on Windows.
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Error K" Security? Follow our step-by-step guide to fix it quickly—no tech expertise needed. Get back to seamless collaboration today!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams Update Error 0x80070002? Discover step-by-step fixes to resolve it quickly. Clear cache, repair files, and get back to seamless updates today!
Tired of Microsoft Teams "Web Error" blocking your browser login? Follow our step-by-step guide with proven fixes to resolve Teams web login issues fast and securely. Get back to work!
Stuck with Microsoft Teams "Error O" Offline? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes to get back online fast. Clear cache, restart, and more – no tech skills needed!
Frustrated by the missing Microsoft Teams icon in Outlook? Learn exactly where to find it, why it disappears, and proven steps to restore it for effortless meetings. Updated for the latest versions!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Windows 10 Error" login issues? Get instant fixes for cache clears, updates, and more. Step-by-step solutions to solve Microsoft Teams login error on Windows 10 fast and frustration-free.
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Website Error" where tabs won’t load? Get step-by-step fixes to resolve it quickly and boost your productivity. Essential troubleshooting for seamless Teams experience.
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Web Error" 503 Service Unavailable? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes for Teams 503 error on web. Get back online fast with our expert guide. Works on all browsers!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Win 7 Error" compatibility? Discover step-by-step fixes to restore seamless video calls and chats on unsupported Windows versions. Quick, reliable solutions inside!
Master troubleshooting Microsoft Teams Breakout Rooms license errors with this step-by-step guide. Quick fixes for common license issues, admin checks, and prevention tips to get your meetings running smoothly.
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Version History" Error? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes to restore access instantly. Clear cache, update Teams, and more—no tech skills needed!
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams Joining Error: Meeting ID Not Found? Get step-by-step fixes to rejoin meetings fast. Updated with the latest Teams patches for seamless collaboration. Solve it now!
Struggling with Microsoft Teams "Video Error" green screen? Discover proven, step-by-step troubleshooting fixes for seamless video calls. Quick solutions inside!
Struggling with the Microsoft Teams "How Teams Works" Tutorial Error? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes to resolve it quickly. Clear cache, update, and more for seamless onboarding. Works on latest versions!
Tired of the frustrating Microsoft Teams "Error Today" on Windows 10? Discover proven, step-by-step fixes to resolve it quickly and restore smooth teamwork. No tech skills needed!