Remote Desktop is a feature available on Windows Pro and Enterprise versions from XP and above, helping you access remote computers within the same LAN, or over the Internet with a few simple setup steps.
In this article, Quantrimang.com will guide you how to use Remote Desktop to access your computer via the Internet on Windows 10 in the most detailed way.
To avoid confusion, in this article we call the computer being remotely accessed the host, the computer used to access the host is the client. The article uses Windows 10 Home to remotely access Windows 10 Pro, Vigor2925 series router.
How to use Remote Desktop in the most detailed way
Below we will go through the detailed setup steps on the two computers, as well as the setup on the router to be able to access the computer remotely over the Internet using Remote Desktop.
1. Setup on host computer
Note: To ensure more security, you need to set a password for the host machine, the more complex the password the better.
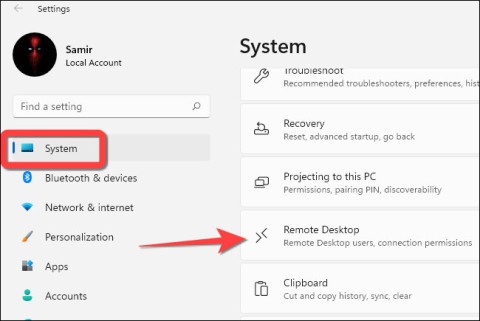
On the computer you want to access remotely, you need to make the following settings:
Step 1: Type remote desktop settings in the search box.
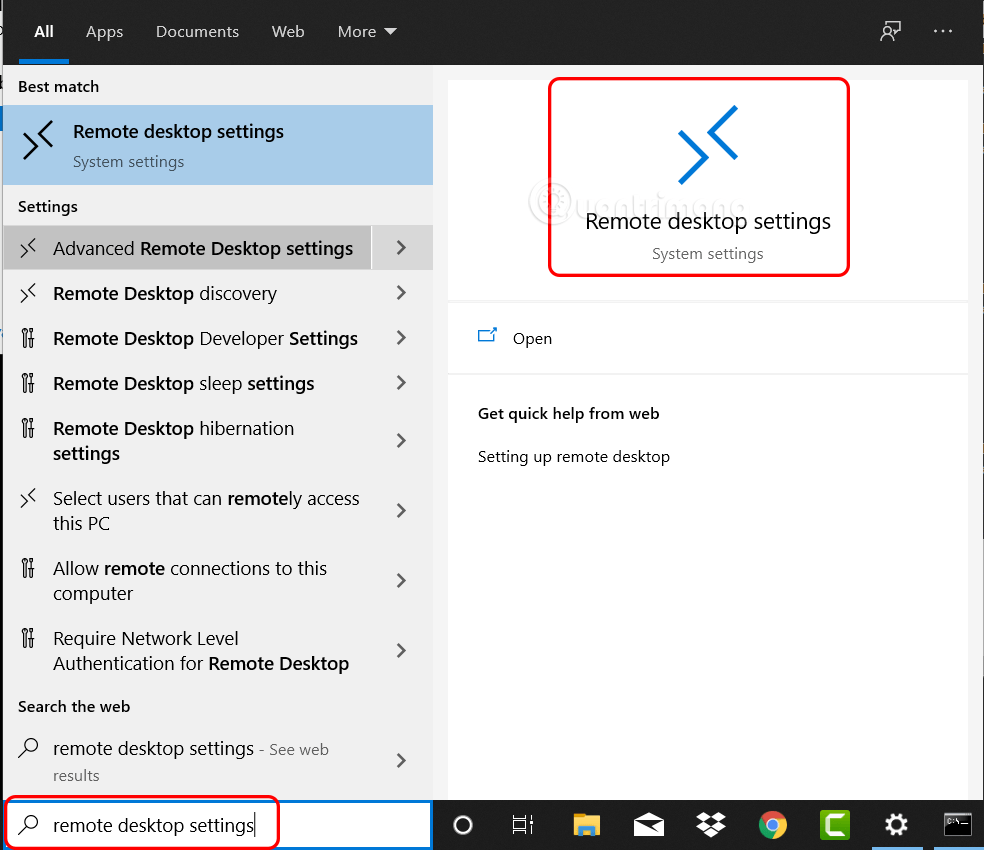
Step 2: Turn on the button below Enable Remote Desktop
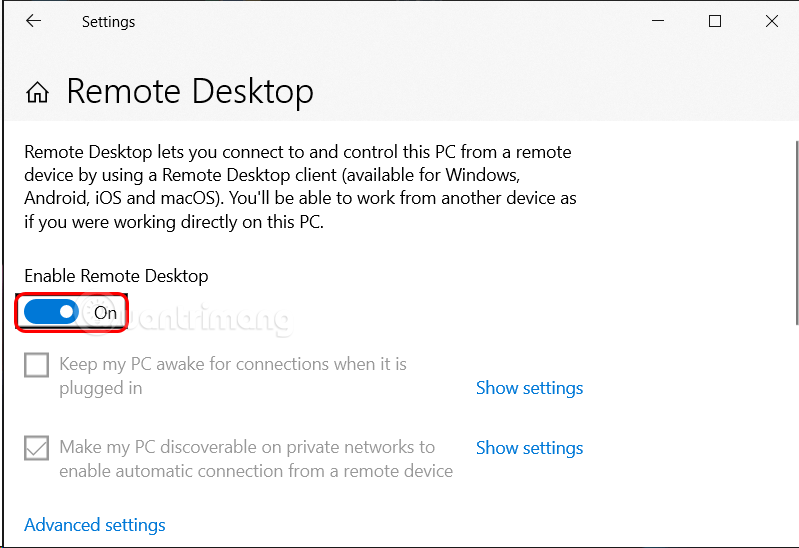
Step 3: Open Command Prompt and enter the command ipconfig
Step 4: If the host machine is connected to a wired network, find the Ethernet adapter Ethernet line, and remember the IP address in the IPv4 Address line as shown below:
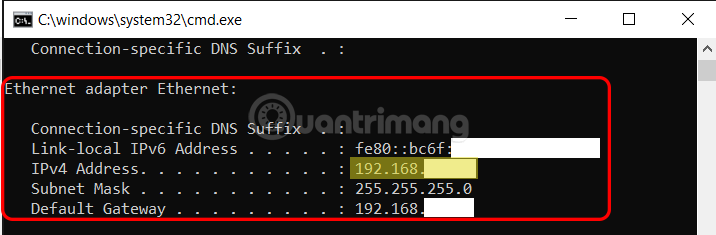
If the host machine uses Wifi, find the Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi line and write down the IPv4 address of the machine.
Step 5: Access the router's administrative address , usually the default is 192.168.1.1 (this address can change depending on the network operator, or the network administrator changes it himself, to know exactly you need to ask the network administrator, or flip the bottom of the router up to see with the home network).
Step 6: Log in to the router management account.
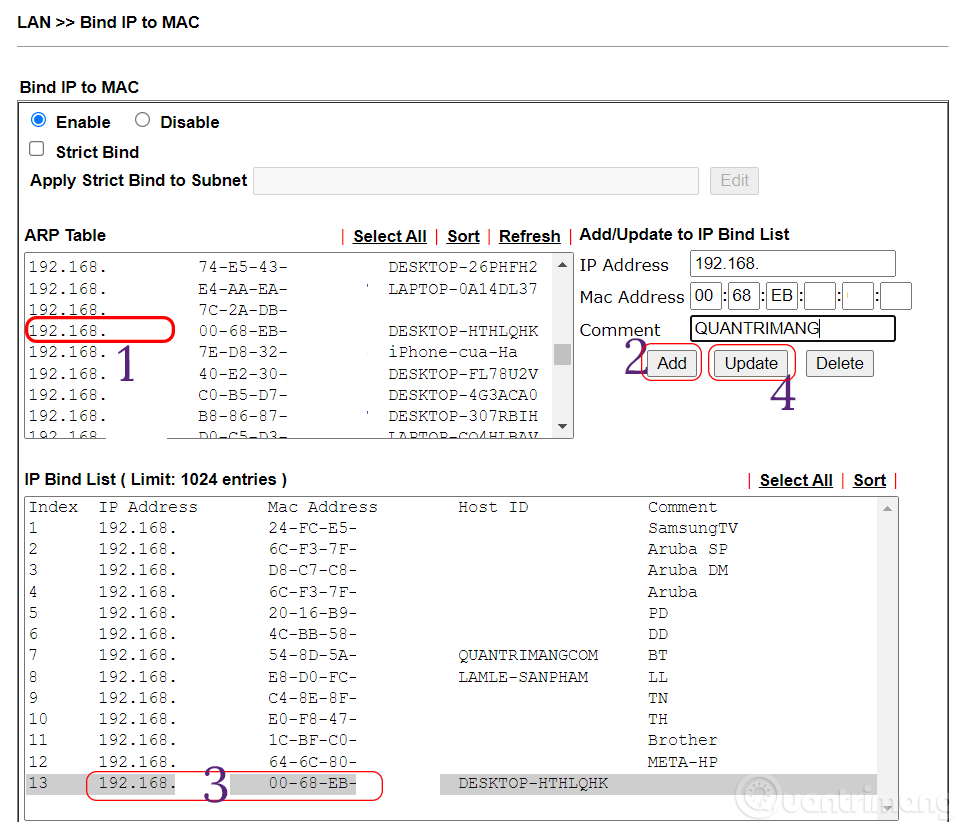
Step 7: Find LAN settings >> then find Bind IP to MAC.
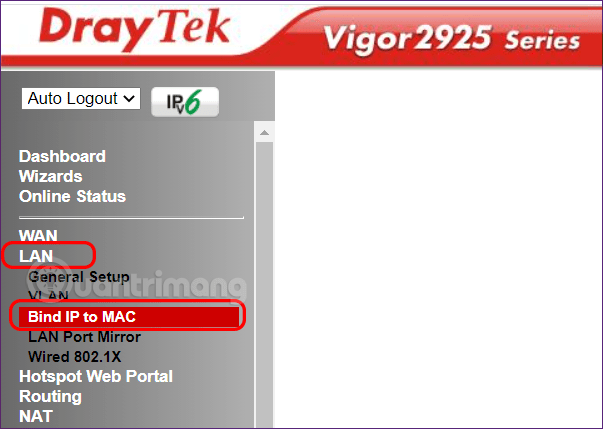
Step 8: In ARP Table , find the IP address recorded in step 4 > click Add to add to the IP Bind List table.
Step 9: In IP Bind List, select the IP address just added > enter a name for the computer to easily identify the computer > click Update > scroll down to the bottom and click OK .
Step 10: Find NAT settings >> then find Port Redirection settings in NAT.
Step 11: Click on the order number you want to add the host machine to, here I click on number 2.
Step 12: Check Enable and enter the following:
- Mode: Single
- Service Name: A memorable name, whatever you want.
- Protocol: TCP/IP
- WAN Interface: ALL
- Public Port: Enter any number and keep this number secret, for example 189.
- Source IP: Any
- Private IP: Enter the IP address in step 4.
- Private Port: 3389 (This is the default port, you can change this default port to another port if needed, detailed instructions below).
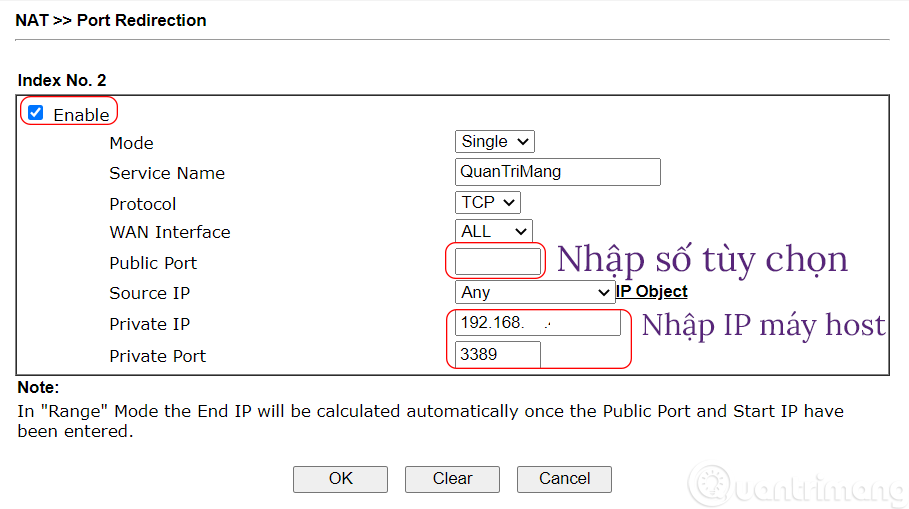
Step 13: Click OK > OK again.
Step 14: Check the host machine's network IP address:
Suppose in this step we have the address: 113.190.91.117.
Change default RDP port
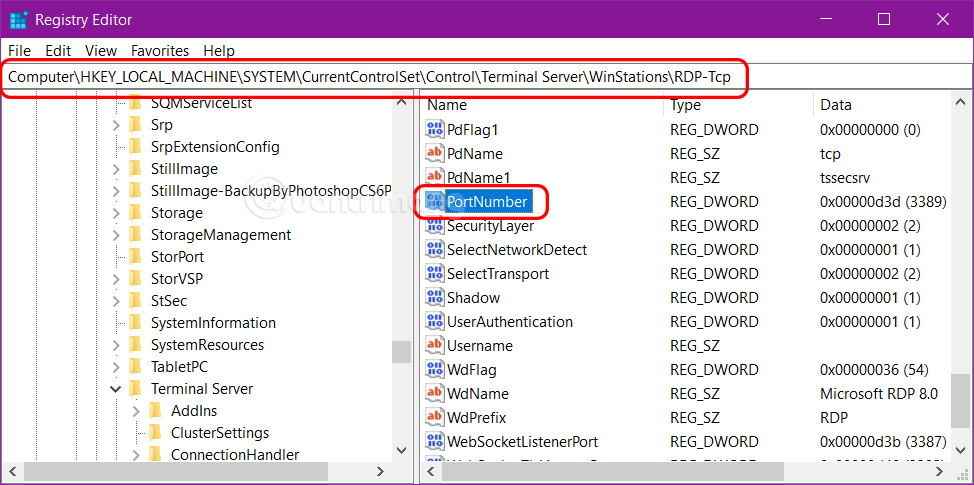
1. On the host computer, press Windows + R > type regedit > Enter .
2. Copy and paste the following path into the Registry Editor window:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
3. Find and double-click PortNumber .
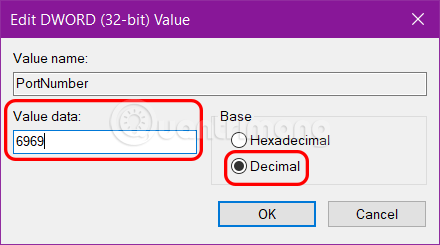
4. In the window that opens, select Decimal and enter a number you want as the new port instead of 3389 > OK .
5. Restart the host computer. If the firewall is on, you must configure the firewall to allow connections to the new port number. Because it is too long, I will write a more detailed tutorial for this part.
6. You can check the current port by running the following PowerShell command:
Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -name "PortNumber"
You can also change the RDP port by running the following PowerShell command . In this command, we will specify the new RDP port as 6969.
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp' -name "PortNumber" -Value 6969
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'RDPPORTLatest' -Profile 'Public' -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 6969
2. Set up on the client machine to access the host via the Internet
On the client computer, do the following:
Step 1: Type Remote Desktop Connection in the search bar and click to open it.
Step 2: In the Computer box, enter:
If the two machines are on the same LAN, you only need to enter the host machine's IP address in step 4 above. If you have changed the default RDP port from 3389 to another port (for example 6969), the address you need to enter now is IP_address_step_4:6969.
If you access another network, enter it in the following format: Network_IP_address (in step 14) : (two dots) Public_Port (you entered in step 12). Then the address you need to enter is: 113.190.91.117:189.
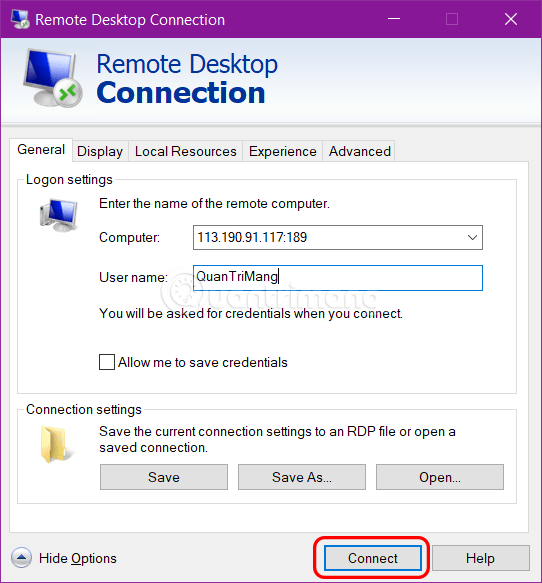
Step 3: Click Connect
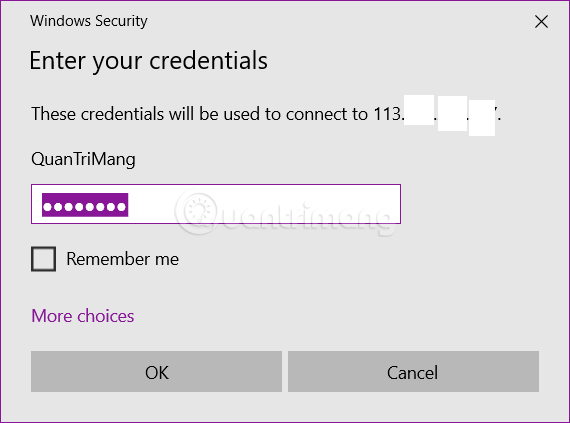
Step 4: Enter password to access host machine
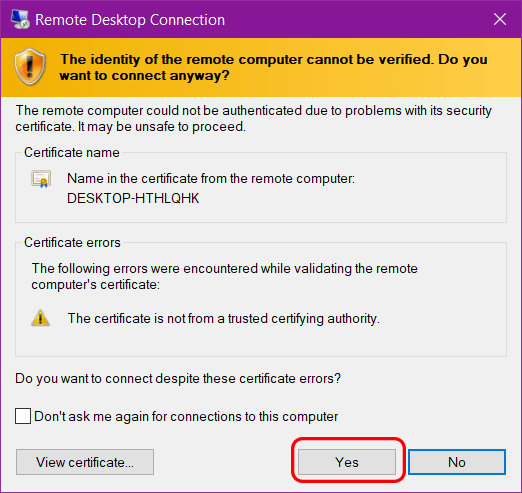
Step 5: Click Yes when this screen appears:
That's it, you have successfully connected to the host machine. Especially with this setup, you can also use your phone to remote the computer , like I often use RD Client.
Some other remote access options
Option 1: Set up a VPN
If you create a virtual private network (VPN) , you won't have to expose the Remote Desktop server directly to the Internet. Instead, when you're away from home, you can connect to the VPN and the computer you're currently working on will act as if it's part of the same local network as your home computer, running the Remote Desktop server. This will allow you to access Remote Desktop and other services that are normally only exposed on a local network.
Quantrimang has covered a few ways to set up your own VPN server , including how to create a VPN server in Windows without any additional software or services .
Setting up a VPN is the safer option when it comes to making Remote Desktop accessible over the Internet, and with the right tools, it's fairly simple to do. However, it's not your only option.
Option 2: Bring the remote computer directly to the Internet
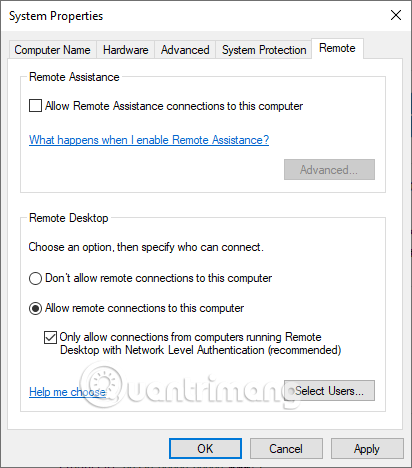
You can also bypass the VPN and expose the Remote Desktop server directly to the Internet by setting up your router to forward traffic from Remote Desktop to the PC being accessed. Obviously, this will expose you to potential attacks over the Internet, so if you choose this route, you'll need to be aware of the risks you're taking. Malware and automated hacking applications are quite prevalent on the Internet and constantly probe your router for weaknesses like open TCP ports, especially the same ones that Remote Desktop uses. At the very least, you should make sure your PC's password is strong, but even then there's still some risk from unpatched vulnerabilities. However, while Quantrimang strongly recommends using a VPN, you can still allow RDP traffic on your router, if that's what you want.
Set up a single computer for remote access
The process is fairly straightforward if you only have one PC that you want to access over the Internet. The computer you set up Remote Desktop on will “listen” for traffic using the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). You’ll need to log into your router, and forward all traffic using TCP port 3389 to the IP address of the PC running Remote Desktop. Since routers have different interfaces, it’s impossible to give you specific instructions. But for more detailed help, be sure to check out Quantrimang ’s detailed guide to port forwarding . Here, we’ll go through a quick example using a basic router.
First, you need to know the IP address of the PC running Remote Desktop that you want to connect to. The easiest way to do this is to fire up the Command Prompt and use the ipconfig command. In the results, look for the details of the network adapter that connects you to the Internet (in this example, it’s “Ethernet Adapter”). In that section, look for the IPv4 address.
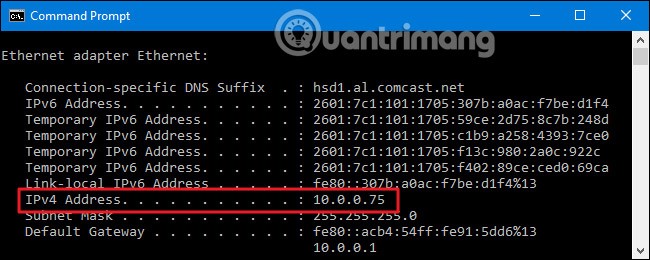
Next, you’ll log into your router and find the Port Forwarding section. The exact location will depend on the router you’re using. In this section, forward TCP port 3389 to the IPv4 address you set earlier.
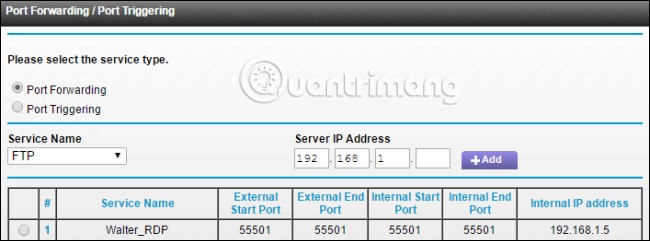
You can now log in to Remote Desktop over the Internet by connecting to the Public IP address that your router displays for your local network.

Remember that IP addresses can be difficult to keep track of (especially if they change), so you may also want to set up a dynamic DNS Service so you can always connect to a domain name that is easy to remember. You may also want to set up a static IP address on the computer running the Remote Desktop server. This will ensure that the computer's internal IP address does not change. If it does, you will need to change your port forwarding configuration.
Change port number or set up multiple computers for remote access
If you have multiple computers on your local network that you want to access remotely over the Internet—or if you have one PC but want to change the default port used for Remote Desktop—you have a few more steps to take. Setting up a VPN is still the better option here, both in terms of ease of setup and security, but there is another way to do it, via port forwarding if you want. The trick is that you'll need to dig into the Registry on each PC, to change the TCP port number it uses to "listen" for Remote Desktop traffic. You then forward ports on your router to each individual computer using the port numbers you've set for them. You can also use this trick even if you only have one PC and want to change from the default, commonly used port number. This is arguably a bit more secure than leaving the default port open.
Before you dive into the Registry, you should also note that some routers allow you to listen for traffic on some external port, but then forward the traffic to another port and your internal PC. For example, you could have your router listen for traffic coming from the Internet on a port like 55,000 and then forward the traffic to a specific computer on your internal network. Using this method, you won't have to change the port each PC uses in the Registry. You can do it all on your router. So check to see if your router supports this first. If it does, skip the Registry section of these instructions.
Assuming you have Remote Desktop set up on each PC and it works for local access, you will need to go to each PC and perform the following steps:
1. Get the IP address for that computer using the procedure outlined above.
2. Use Registry Editor to change the remote listening port number on that computer.
3. Make a note of which port number goes with which IP address.
Here’s how to do the Registry part of those steps, and the usual standard warning: Registry Editor is a powerful tool, and misusing it can render your system unstable or even inoperable. This is a fairly simple procedure, and as long as you follow the instructions, you shouldn’t have any problems. That said, if you’ve never worked with it before, read up on how to use Registry Editor before you get started, and be sure to back up the Registry (and your computer) before making changes.
Open Registry Editor by clicking Start and typing "regedit". Press Enter to open Registry Editor and allow it to make changes to your computer.
In Registry Editor , use the left sidebar to navigate to the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber
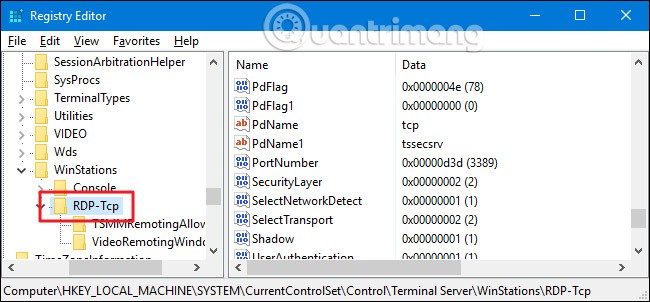
On the right, double-click the PortNumber value to open its properties window.
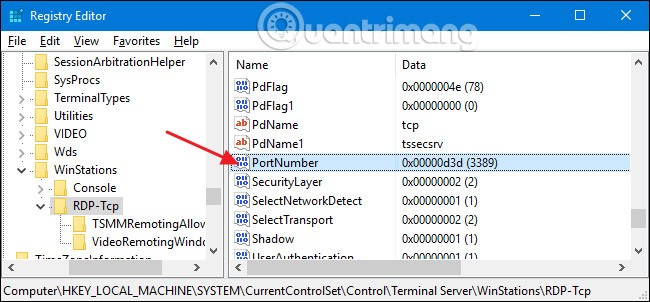
In the properties window, select the “Decimal” option and then enter the port number you want to use. The port number you choose is up to you, but be aware that some port numbers are already in use. You can check Wikipedia’s list of common ports to see which ones you should not use. However, network applications installed on your computer may use additional ports. Port numbers can go up to 65,535, so if you choose a port number above 50,000, you should be safe. Once you have entered the port number you want to use, click “OK.”
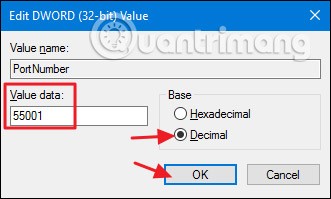
You can now close Registry Editor. Make a note of the port number you used, the IP address, and the computer name. Then move on to the next PC.
Once you've finished changing the ports on all your PCs, you can log into your router and start forwarding each port to the associated computer. If your router allows it, you should also enter the name of the computer. You can always use the “Application” entry , which most routers have a feature that keeps track of which application is assigned to the port. Just enter the name of the computer followed by an extension like "_RDP" and you'll be fine.
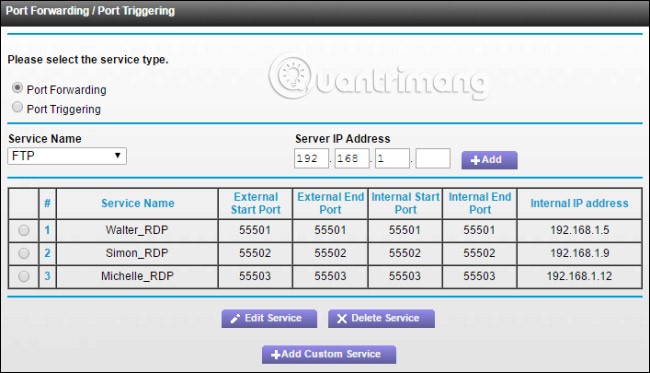
Once everything is set up, you can log into Remote Desktop over the Internet by connecting to the Public IP address that your router uses on your local network, followed by a colon and the port number for the computer you want to connect to. For example, if your Public IP is 123.45.67.89 and you set your PC to port number 55501, it will connect to “123.45.67.89:55501”.
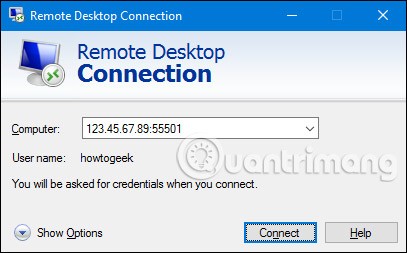
Of course, you can always save that connection in Remote Desktop by name, so you don't have to enter the IP address and port number every time you access it.
It takes a bit of setup to get Remote Desktop working over the Internet, especially if you're not using a VPN or even if you have multiple computers you want to access. However, once you're done with the setup, Remote Desktop gives you a powerful and reliable way to access your computer remotely without requiring any additional services.
What is Remote Desktop?
The term Remote Desktop refers to the ability to remotely connect a computer to another computer and control its screen, as if the user were sitting in front of the remote computer. Remote Desktop is usually accessed through port 3389 and uses software that comes with Windows or some third-party programs, such as TeamViewer , PC Anywhere, VNC , and other similar software.
All versions of Windows operating systems are equipped with the Remote Desktop feature. However, to be able to use this feature, you will have to activate it first.
Good luck!
See also: